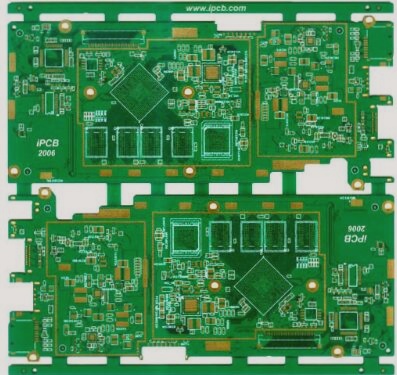
1. All components, mounting holes, and positioning holes are labeled with corresponding silk screen markings to facilitate the installation of the finished PCB. Mounting holes are marked on the PCB with identifiers such as H1, H2, …, Hn for easy recognition.
2. Silk screen characters should be arranged from left to right and bottom to top whenever possible. For polarized components like electrolytic capacitors and diodes, ensure they are oriented consistently within each functional unit.

3. The device pad and tin track requiring tinning should not have any silk screen, and the device number should remain visible and unobstructed after installation. (In high-density designs, this is essential except for areas where silk screen printing is unnecessary.) To ensure reliable soldering, the device pad must be free of silk screen. Additionally, to maintain the continuity of the tin-lined track, it should also be free from silk screen. Device insertion and maintenance should be facilitated by ensuring the device number is not obscured post-installation. Silk screen should not cover via holes or pads to prevent partial loss during soldering, which could affect functionality. The screen spacing should be greater than 5 mils.
4. The polarity of polarized components should be clearly indicated on the silk screen, with polarity direction marks easily identifiable.
5. The direction of directional connectors should be clearly marked on the silk screen.
6. The PCB board should include a barcode position mark. When space permits, a 42*6 barcode screen printing frame should be included, with the barcode positioned for easy scanning.
7. The board information, such as PCB name, date, and version number, should be clearly printed on the PCB board. The PCB board file should include these details, with clear and prominent placement on the finished board.
8. The PCB board should display complete relevant information and the anti-static logo of the manufacturer.
9. The number of light-painting files on the PCB board must be correct. Each layer should have the proper output, and the total number of layers should be accurately represented.
10. The device identifiers on the PCB must match those in the BOM list.
**Design Printout Considerations**
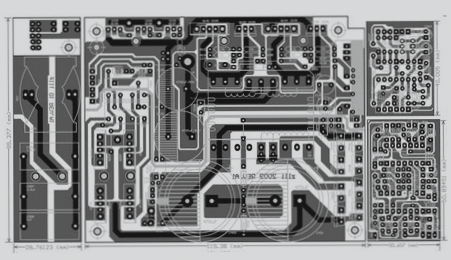
1. The required layers for output are:
(1) Wiring layers, including top layer, bottom layer, middle wiring layers, and power layers (VCC and GND layers);
(2) Silk screen layers, including top silk screen and bottom silk screen;
(3) Solder mask layers, including top solder mask and bottom solder mask;
(4) Additionally, generate the drilling file NCDrill.
2. If the power layer is set to Split/Mixed, select Routing in the Document item of the AddDocument window and use PourManager’s Plane Connect to copper-clad the PCB board before each output of the light drawing file. If set to CAMPlane, select Plane in the Layer item, add Layer25, and choose Pads and Vias in Layer25.
3. In the Device Setup window, change the value of Aperture to 199.
4. When setting the Layer of each layer, select Board Outline.
5. Do not select Part Type when setting the Layer of the silkscreen layer. Instead, select the Outline Text Line for the top and bottom layers, as well as the silkscreen layer.
6. When setting the Layer of the solder mask layer, indicate via holes where no solder mask is added, and select via holes where the solder mask is applied based on specific requirements.
7. Use the default settings of the PowerPCB board when generating the drilling file and avoid making any changes.
8. After output, open all light-drawing files with CAM350, and have designers and reviewers print and check them according to the “PCB Board Checklist.”
**Safety Marking Requirements**
1. The fuse safety regulations must be complete, with six signs near the fuse, including the fuse serial number, fusing characteristics, rated current value, explosion-proof characteristics, rated voltage value, and English warning signs. If space on the PCB board does not permit English warning signs, they can be included in the product instruction manual.
2. The dangerous voltage area on the PCB board should be marked with a high voltage warning sign. The dangerous voltage area should be separated from the safe voltage area by a 40 mil wide dotted line.
3. The original and auxiliary side isolation belts should be clearly marked, with a dotted line separating them.
4. The safety label on the PCB board should be clear and complete.
2. Silk screen characters should be arranged from left to right and bottom to top whenever possible. For polarized components like electrolytic capacitors and diodes, ensure they are oriented consistently within each functional unit.

3. The device pad and tin track requiring tinning should not have any silk screen, and the device number should remain visible and unobstructed after installation. (In high-density designs, this is essential except for areas where silk screen printing is unnecessary.) To ensure reliable soldering, the device pad must be free of silk screen. Additionally, to maintain the continuity of the tin-lined track, it should also be free from silk screen. Device insertion and maintenance should be facilitated by ensuring the device number is not obscured post-installation. Silk screen should not cover via holes or pads to prevent partial loss during soldering, which could affect functionality. The screen spacing should be greater than 5 mils.
4. The polarity of polarized components should be clearly indicated on the silk screen, with polarity direction marks easily identifiable.
5. The direction of directional connectors should be clearly marked on the silk screen.
6. The PCB board should include a barcode position mark. When space permits, a 42*6 barcode screen printing frame should be included, with the barcode positioned for easy scanning.
7. The board information, such as PCB name, date, and version number, should be clearly printed on the PCB board. The PCB board file should include these details, with clear and prominent placement on the finished board.
8. The PCB board should display complete relevant information and the anti-static logo of the manufacturer.
9. The number of light-painting files on the PCB board must be correct. Each layer should have the proper output, and the total number of layers should be accurately represented.
10. The device identifiers on the PCB must match those in the BOM list.
**Design Printout Considerations**
1. The required layers for output are:
(1) Wiring layers, including top layer, bottom layer, middle wiring layers, and power layers (VCC and GND layers);
(2) Silk screen layers, including top silk screen and bottom silk screen;
(3) Solder mask layers, including top solder mask and bottom solder mask;
(4) Additionally, generate the drilling file NCDrill.
2. If the power layer is set to Split/Mixed, select Routing in the Document item of the AddDocument window and use PourManager’s Plane Connect to copper-clad the PCB board before each output of the light drawing file. If set to CAMPlane, select Plane in the Layer item, add Layer25, and choose Pads and Vias in Layer25.
3. In the Device Setup window, change the value of Aperture to 199.
4. When setting the Layer of each layer, select Board Outline.
5. Do not select Part Type when setting the Layer of the silkscreen layer. Instead, select the Outline Text Line for the top and bottom layers, as well as the silkscreen layer.
6. When setting the Layer of the solder mask layer, indicate via holes where no solder mask is added, and select via holes where the solder mask is applied based on specific requirements.
7. Use the default settings of the PowerPCB board when generating the drilling file and avoid making any changes.
8. After output, open all light-drawing files with CAM350, and have designers and reviewers print and check them according to the “PCB Board Checklist.”
**Safety Marking Requirements**
1. The fuse safety regulations must be complete, with six signs near the fuse, including the fuse serial number, fusing characteristics, rated current value, explosion-proof characteristics, rated voltage value, and English warning signs. If space on the PCB board does not permit English warning signs, they can be included in the product instruction manual.
2. The dangerous voltage area on the PCB board should be marked with a high voltage warning sign. The dangerous voltage area should be separated from the safe voltage area by a 40 mil wide dotted line.
3. The original and auxiliary side isolation belts should be clearly marked, with a dotted line separating them.
4. The safety label on the PCB board should be clear and complete.