1. Rigid-flex PCB stack-up integrates rigid and flexible layers, comprising three or more layers of bonded materials.
2. Rigid substrates impart mechanical strength to the circuit boards, while flexible substrates mitigate heat, vibration, and humidity.

Features of rigid-flex PCB stack-up
1. Fewer solder joints and connectors
Rigid-flex stack-ups feature fewer solder joints and connectors compared to traditional printed circuit boards. This reduces the risk of soldering errors, which can otherwise necessitate costly rework of flexible PCB components or lead to circuit failures.
2. Minimum board thickness
These rigid-flex technologies utilize thin films to effectively reduce board thickness without compromising quality or reliability. Board thickness typically ranges from 0.2mm to 0.4mm, enhancing durability.
3. High thermal strength
Rigid-flex PCBs offer superior heat dissipation and increased reliability compared to conventional rigid boards.
4. High aspect ratio
A high aspect ratio describes a scenario where width exceeds height, allowing more space between components on the circuit board, thereby aiding signal transmission. Moreover, a high aspect ratio facilitates easier wiring of traces and components.
Advantages of Rigid-flex PCB stack-up
Rigid and flexible designs not only grant 3D freedom to flexible circuit boards, now a standard specification, but also offer additional benefits such as reduced maintenance and consistent electrical configuration. Rigid and flex PCBs also promote optimized enclosure solutions.
1. Enhanced durability and flexibility
Flexibility and durability are crucial aspects of PCB stack-up. The flexibility of PCB stack-up depends on layer count and material selection. Rigid-flex stack-ups aim to mitigate PCB strain that could otherwise compromise circuit integrity. These boards exhibit excellent mechanical and dielectric properties, coupled with a broad operating temperature range, ensuring robust durability.
2. Space efficiency
Space efficiency is paramount in rigid and flexible designs. By saving space and reducing production costs, stacking rigid PCBs with thin and expansive surface areas enables intricate circuitry implementation without compromising the efficiency of flexible circuits.
The integration of rigid and flexible elements enhances overall PCB structure, effectively improving bending stiffness and flexural performance. This approach ensures heightened stability and reliability during operation.
2. Rigid substrates impart mechanical strength to the circuit boards, while flexible substrates mitigate heat, vibration, and humidity.
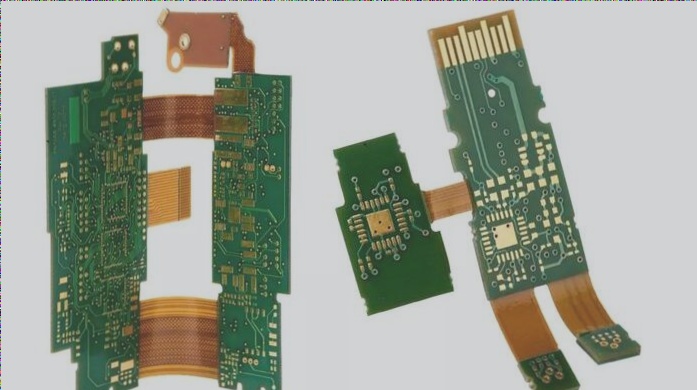
Features of rigid-flex PCB stack-up
1. Fewer solder joints and connectors
Rigid-flex stack-ups feature fewer solder joints and connectors compared to traditional printed circuit boards. This reduces the risk of soldering errors, which can otherwise necessitate costly rework of flexible PCB components or lead to circuit failures.
2. Minimum board thickness
These rigid-flex technologies utilize thin films to effectively reduce board thickness without compromising quality or reliability. Board thickness typically ranges from 0.2mm to 0.4mm, enhancing durability.
3. High thermal strength
Rigid-flex PCBs offer superior heat dissipation and increased reliability compared to conventional rigid boards.
4. High aspect ratio
A high aspect ratio describes a scenario where width exceeds height, allowing more space between components on the circuit board, thereby aiding signal transmission. Moreover, a high aspect ratio facilitates easier wiring of traces and components.
Advantages of Rigid-flex PCB stack-up
Rigid and flexible designs not only grant 3D freedom to flexible circuit boards, now a standard specification, but also offer additional benefits such as reduced maintenance and consistent electrical configuration. Rigid and flex PCBs also promote optimized enclosure solutions.
1. Enhanced durability and flexibility
Flexibility and durability are crucial aspects of PCB stack-up. The flexibility of PCB stack-up depends on layer count and material selection. Rigid-flex stack-ups aim to mitigate PCB strain that could otherwise compromise circuit integrity. These boards exhibit excellent mechanical and dielectric properties, coupled with a broad operating temperature range, ensuring robust durability.
2. Space efficiency
Space efficiency is paramount in rigid and flexible designs. By saving space and reducing production costs, stacking rigid PCBs with thin and expansive surface areas enables intricate circuitry implementation without compromising the efficiency of flexible circuits.
The integration of rigid and flexible elements enhances overall PCB structure, effectively improving bending stiffness and flexural performance. This approach ensures heightened stability and reliability during operation.