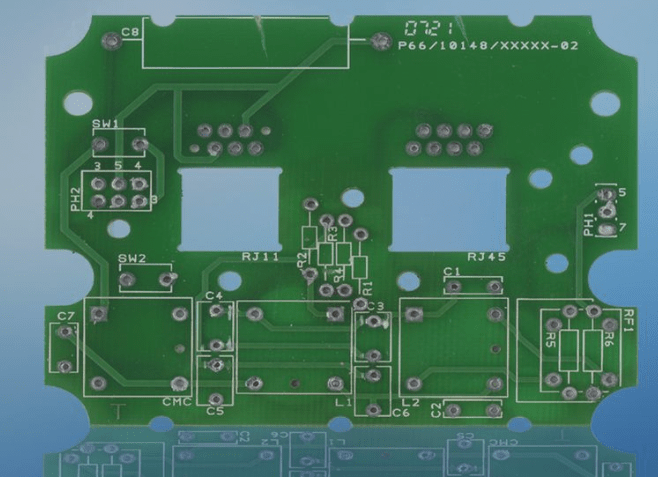
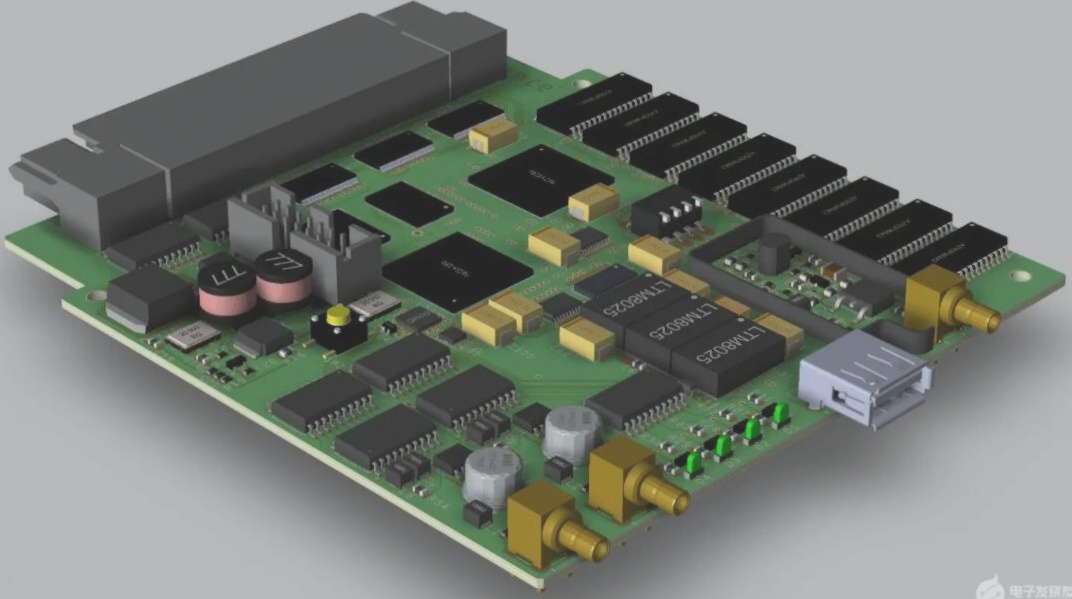
What is the standard for PCBA board inspection in the SMT patch workshop? Below is a comprehensive list of PCBA inspection items relevant to the SMT patch workshop.
1. Empty solder joints of SMT components
2. Cold solder joints on SMT components: Lightly touch the component pins with a toothpick.
3. Short circuits (solder bridges) between SMT component solder points
4. Absence of SMT components
5. Incorrect SMT component types
6. Reversed or incorrect polarity of SMT components leading to potential combustion or explosion
7. Overlapping SMT components

8. SMT parts overturned: the text side is facing downward.
9. SMT parts standing side by side: chip element length ≤ 3mm, width ≤ 1.5mm, no more than five (MI).
10. Tombstoning of SMT parts: the end of the chip component is elevated.
11. SMT parts foot offset: the lateral offset is less than or equal to 1/2 of the width of the solderable end.
12. SMT parts floating height: the distance between the bottom of the component and the substrate is <>.
13. SMT parts foot tilt: the height of the tilt exceeds the thickness of the part foot.
14. The heel of SMT parts is uneven and not tinned.
15. SMT parts are unidentifiable (printing is unclear).
16. SMT parts foot or body shows signs of oxidation.
17. SMT parts body damage: capacitor damage (MA); resistance damage is less than 1/4 of the component’s width or thickness (MI); IC damage in any orientation.
18. SMT parts sourced from non-designated suppliers: as per BOM, ECN.
19. SMT parts solder point tin height: the height of the tin tip exceeds the height of the component body.
20. SMT parts insufficient tin: the minimum solder joint height is less than the solder thickness plus 25% of the height of the solderable end, or the solder thickness plus 0.5mm, whichever is smaller (MA).
21. SMT parts excessive tin: the maximum solder joint height exceeds the pad or rises to the top of the solderable end of the metal plating end cap, which is acceptable, with solder making contact with the component body (MA).
22. Tin ball/tin dross: more than five solder balls or solder splashes (0.13mm or smaller) per 600mm² is (MA).
23. Solder joints with pinholes/blow holes: one solder joint exhibiting more than one (inclusive) is (MI).
24. Crystallization phenomenon: white residues are present on the surface of the PCB, solder terminals, or around the terminals, along with white crystals on the metal surface.
25. The board surface is unclean: any uncleanness that cannot be detected from a long arm distance within 30 seconds is acceptable.
26. Poor dispensing: glue is positioned in the welding area, reducing the width of the weldable end by more than 50%.
27. PCB copper foil delamination.
28. PCB exposed copper: circuit (gold finger) exposed copper width exceeding 0.5mm is (MA).
29. PCB scratches: no substrate is visible through scratches.
30. PCB scorching: discoloration occurs when the PCB is burned and yellowed after passing through the reflow oven or repair process, resulting in a color difference.
31. PCB bending: deformation exceeding 1mm per 300mm in any direction is (MA).
32. PCB inner layer separation (bubble): the area of blistering and delamination does not exceed 25% (MI) of the distance between the plating holes or internal wires; foaming between through holes or internal wires is (MA).
33. PCB with foreign matter: conductive (MA); non-conductive (MI).
34. PCB version discrepancy: as per BOM, ECN.
35. Gold finger tinning: the tin dip position is within 80% of the edge of the board (MA).
1. Empty solder joints of SMT components
2. Cold solder joints on SMT components: Lightly touch the component pins with a toothpick.
3. Short circuits (solder bridges) between SMT component solder points
4. Absence of SMT components
5. Incorrect SMT component types
6. Reversed or incorrect polarity of SMT components leading to potential combustion or explosion
7. Overlapping SMT components
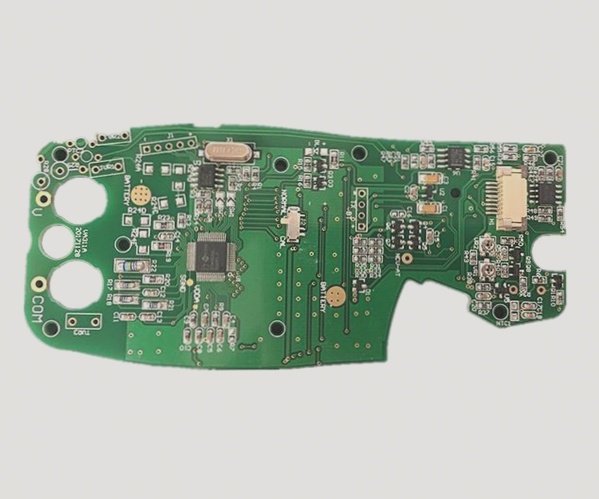
8. SMT parts overturned: the text side is facing downward.
9. SMT parts standing side by side: chip element length ≤ 3mm, width ≤ 1.5mm, no more than five (MI).
10. Tombstoning of SMT parts: the end of the chip component is elevated.
11. SMT parts foot offset: the lateral offset is less than or equal to 1/2 of the width of the solderable end.
12. SMT parts floating height: the distance between the bottom of the component and the substrate is <>.
13. SMT parts foot tilt: the height of the tilt exceeds the thickness of the part foot.
14. The heel of SMT parts is uneven and not tinned.
15. SMT parts are unidentifiable (printing is unclear).
16. SMT parts foot or body shows signs of oxidation.
17. SMT parts body damage: capacitor damage (MA); resistance damage is less than 1/4 of the component’s width or thickness (MI); IC damage in any orientation.
18. SMT parts sourced from non-designated suppliers: as per BOM, ECN.
19. SMT parts solder point tin height: the height of the tin tip exceeds the height of the component body.
20. SMT parts insufficient tin: the minimum solder joint height is less than the solder thickness plus 25% of the height of the solderable end, or the solder thickness plus 0.5mm, whichever is smaller (MA).
21. SMT parts excessive tin: the maximum solder joint height exceeds the pad or rises to the top of the solderable end of the metal plating end cap, which is acceptable, with solder making contact with the component body (MA).
22. Tin ball/tin dross: more than five solder balls or solder splashes (0.13mm or smaller) per 600mm² is (MA).
23. Solder joints with pinholes/blow holes: one solder joint exhibiting more than one (inclusive) is (MI).
24. Crystallization phenomenon: white residues are present on the surface of the PCB, solder terminals, or around the terminals, along with white crystals on the metal surface.
25. The board surface is unclean: any uncleanness that cannot be detected from a long arm distance within 30 seconds is acceptable.
26. Poor dispensing: glue is positioned in the welding area, reducing the width of the weldable end by more than 50%.
27. PCB copper foil delamination.
28. PCB exposed copper: circuit (gold finger) exposed copper width exceeding 0.5mm is (MA).
29. PCB scratches: no substrate is visible through scratches.
30. PCB scorching: discoloration occurs when the PCB is burned and yellowed after passing through the reflow oven or repair process, resulting in a color difference.
31. PCB bending: deformation exceeding 1mm per 300mm in any direction is (MA).
32. PCB inner layer separation (bubble): the area of blistering and delamination does not exceed 25% (MI) of the distance between the plating holes or internal wires; foaming between through holes or internal wires is (MA).
33. PCB with foreign matter: conductive (MA); non-conductive (MI).
34. PCB version discrepancy: as per BOM, ECN.
35. Gold finger tinning: the tin dip position is within 80% of the edge of the board (MA).