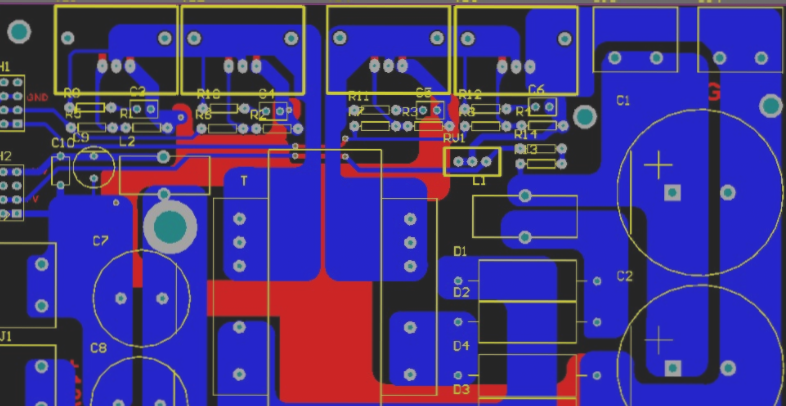
2.54mm (100mil), 5.08mm (200mil), 7.62mm (300mil), the thickness of tin can be measured by micro-slicing: after fine polishing, use the micro-etching method to find the IMC thickness between copper-tin alloys, and prepare the micro-etching potion. The volume ratio of hydrogen peroxide and ammonia water is 1:3 for micro-etching for 10-15 seconds. The thickness of the interface alloy is generally 6 micro inches for one tin spray, and about 1.8 micro inches for the second time. The thickness of the tin spray can be measured by x-ray fluorescence thickness gauge measurement. The flatness of the board mainly includes boards bending (bow board warping in the long direction) and board warping (twist, board diagonal warping). The size of the board changes.
The thickness of tin that can be retained on the pad is affected by two factors:
1. The hole wall is drawn or extended by the inner flat ring, which will cause a heat sink effect so that the sprayed molten tin is easier to cool and solidify, and the solid tin layer is thicker. Generally, there are no holes. The tin thickness that can be maintained in the plated through-hole of the inner flat ring does not seem to be significantly related to the aspect ratio of the through-hole. The tin thickness at the corner of the hole is about 0.75 microns and 30 microinches, from the two ends of the hole to the corner to the hole in the center, the tin thickness gradually increases. The reduction of the aperture is about 18-30 microns, and the center of the hole shrinks most significantly, where the tin layer is the thickest.
2. The thickness of IMC tin spraying at one time is 6 micro-inches. These three data are the best tools to check the suitability of the horizontal spray tin temperature curve. The changes of the three are related to the temperature. The IMC is Cu6Sn5 of eta phase, which has good soldering performance, and Cu3Sn of malignant episilon phase. Good pretreatment is conducive to the formation of a good alloy layer. The Cu3Sn of the malignant episilon phase is positively related to the time of tin spraying and the thickness of tin spraying.
The flatness of the board is mainly affected by the following factors:
a. Whether the thickness of the board is different and the arrangement of the layers is symmetrical or not.
The thickness of tin that can be retained on the pad is affected by two factors:
1. The hole wall is drawn or extended by the inner flat ring, which will cause a heat sink effect so that the sprayed molten tin is easier to cool and solidify, and the solid tin layer is thicker. Generally, there are no holes. The tin thickness that can be maintained in the plated through-hole of the inner flat ring does not seem to be significantly related to the aspect ratio of the through-hole. The tin thickness at the corner of the hole is about 0.75 microns and 30 microinches, from the two ends of the hole to the corner to the hole in the center, the tin thickness gradually increases. The reduction of the aperture is about 18-30 microns, and the center of the hole shrinks most significantly, where the tin layer is the thickest.
2. The thickness of IMC tin spraying at one time is 6 micro-inches. These three data are the best tools to check the suitability of the horizontal spray tin temperature curve. The changes of the three are related to the temperature. The IMC is Cu6Sn5 of eta phase, which has good soldering performance, and Cu3Sn of malignant episilon phase. Good pretreatment is conducive to the formation of a good alloy layer. The Cu3Sn of the malignant episilon phase is positively related to the time of tin spraying and the thickness of tin spraying.
The flatness of the board is mainly affected by the following factors:
a. Whether the thickness of the board is different and the arrangement of the layers is symmetrical or not.