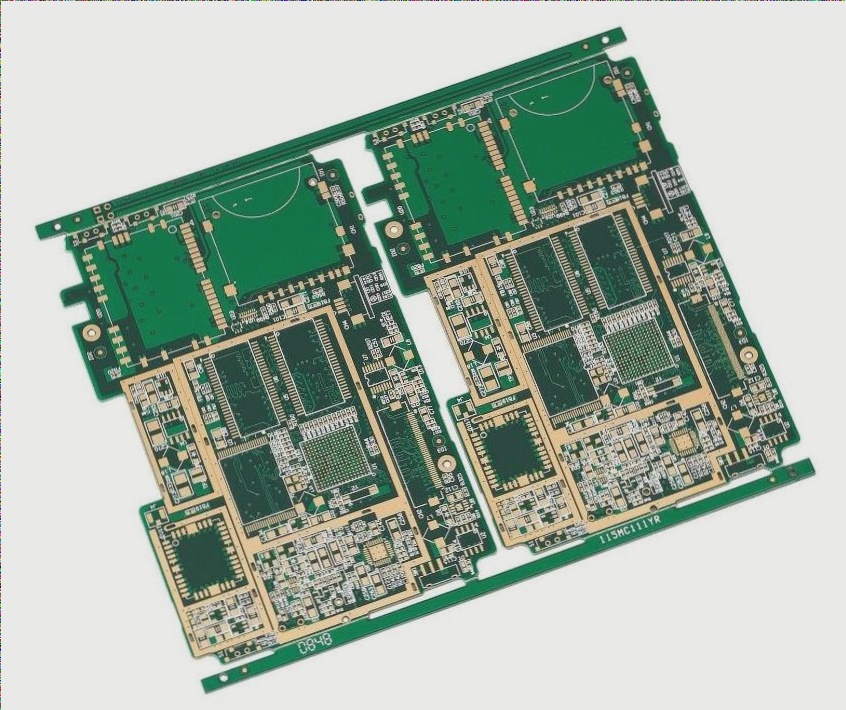
The Challenges of Electronic Product Assembly
Electronic product assembly poses significant challenges in production and operation scheduling due to the vast array of components and the short life cycle of electronic products. The current mainstream production mode in electronic manufacturing involves multiple varieties, small batches, and variable batches. The time spent switching between multiple varieties has become a significant portion of the overall assembly time.
Key Components of PCB Assembly Line
- High-speed placement machine
- Multi-functional placement machine
- Board feeders
- Screen printers
- Glue dispensers
- Reflow soldering and curing ovens
- Board unwinders
The PCB assembly line is comprised of these essential equipment connected in a series. While auxiliary equipment plays a crucial role, they do not represent bottleneck processes and are omitted during modeling.
Efficiency in Component Placement
During the placement process, components for different PCB types are placed on feeding troughs. The pick-and-place device then mounts the components onto designated positions on the PCB. High-speed placement machines and multi-functional placement machines have varying component placement and feeder switch times, which are critical factors in the assembly process.
Optimizing Production Scheduling
In a multi-variety, small-batch environment, PCBs are grouped based on similar characteristics to minimize feeder changes and switching times during assembly. Production scheduling is divided into board-level and group-level scheduling to streamline the production order among PCBs within a group and between PCB groups.