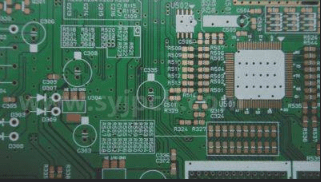
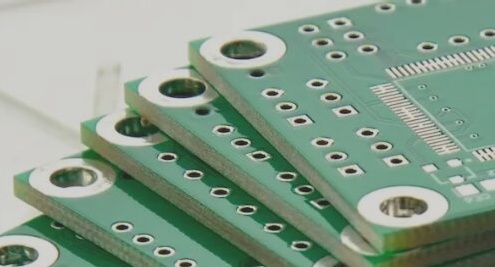
PCB multi-substrate design
PCB multi-substrate design closely resembles single or dual-substrate designs, emphasizing the importance of avoiding overly dense circuit layouts to prevent issues with tolerances, inner layer capacity, and product safety; thus, performance evaluations should consider thermal shock, insulation resistance, and solderability, among other critical factors.