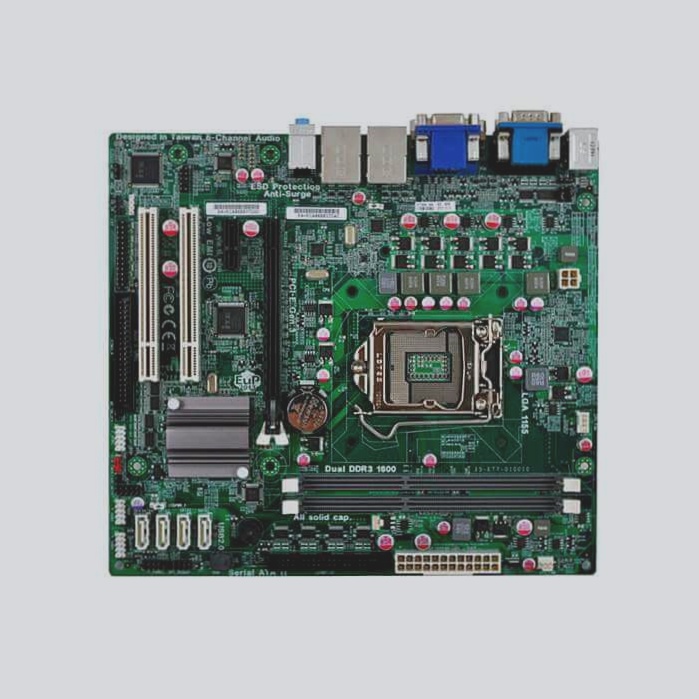
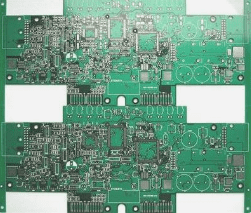
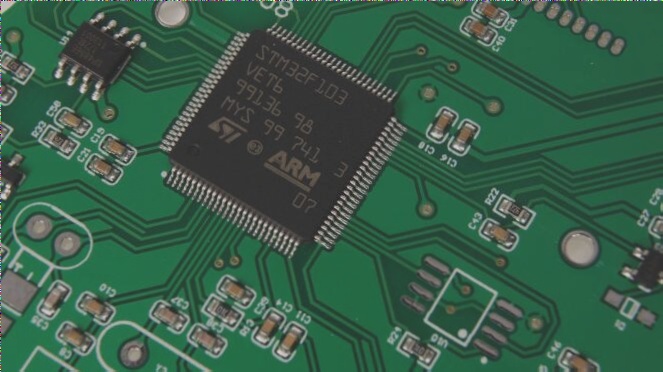
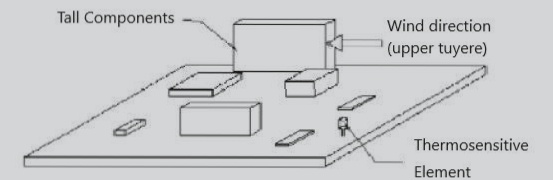
Versatile Applications in Circuit Board Design
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a crucial component in electronics, featuring conductive pathways on an insulating substrate, enabling electrical connections and supporting various electronic components.



 العربية
العربية 简体中文
简体中文 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español ไทย
ไทย