What is the Heat Dissipation System in a PCB Board?
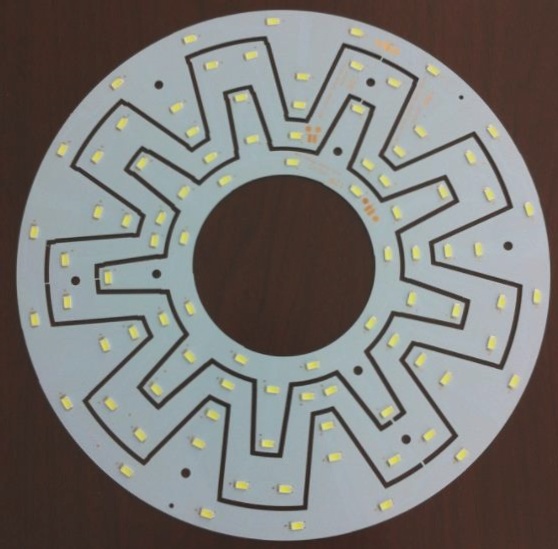
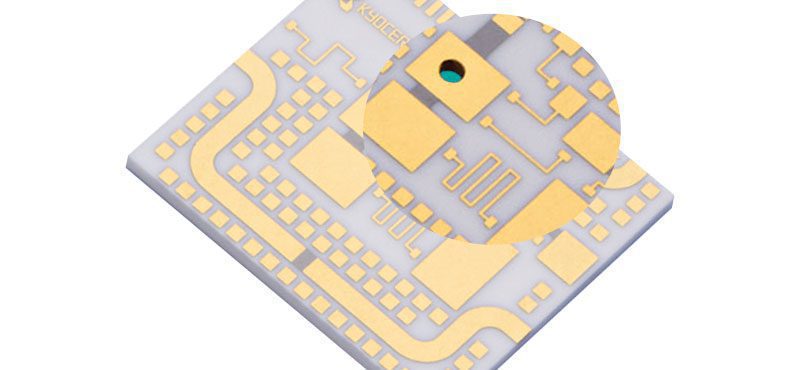
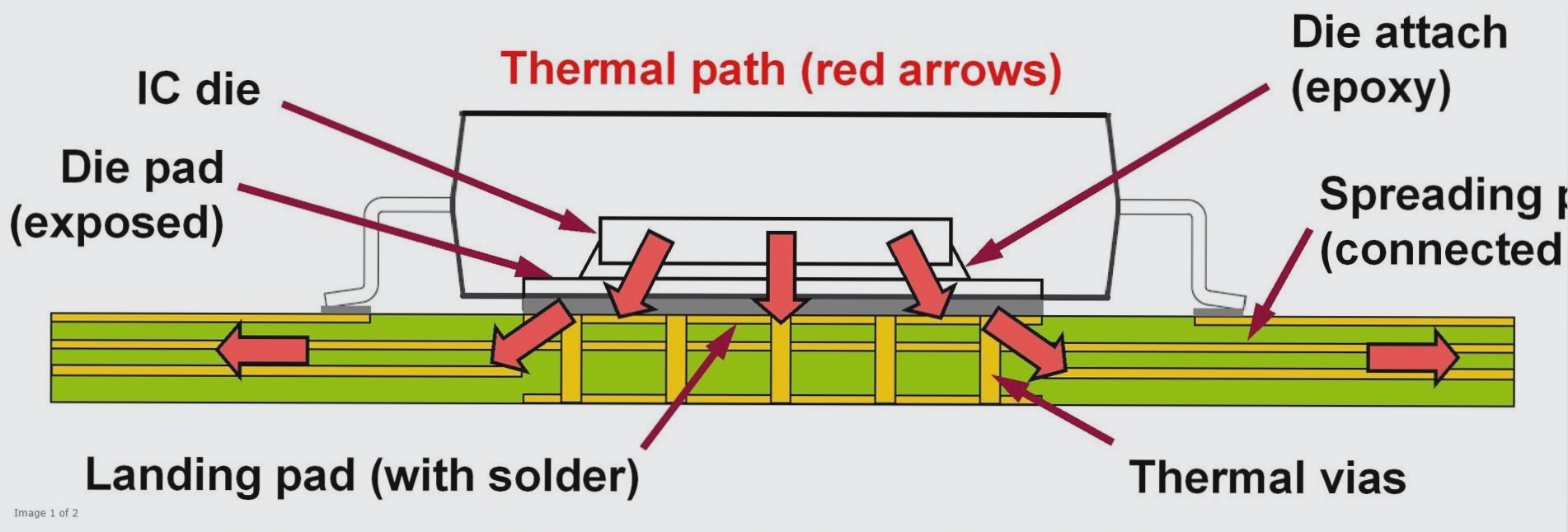
In PCB board design, heat dissipation is crucial and can be achieved through various cooling methods, selection of components, and consideration of the coefficient of thermal expansion. WellCircuits Limited specializes in producing high-precision circuit boards to meet the diverse needs of customers in different industries, offering solutions such as blind buried vias, thick copper boards, and various types of circuit boards including HDI and rigid-flex combinations.
What is the Heat Dissipation System in a PCB Board? Read More »