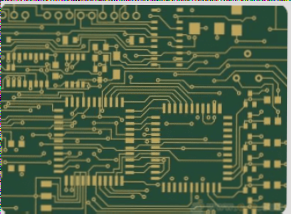
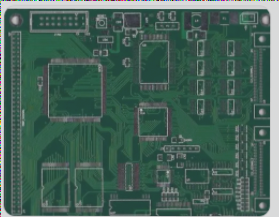
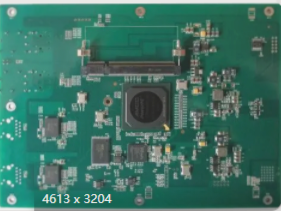
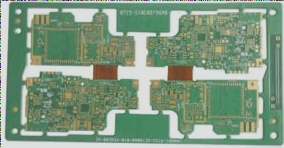
Practical Guidelines for PCB Layout and Routing
High-integrity PCB design for high-speed circuits requires careful attention to layout, component placement, and power bypassing to ensure optimal performance and minimize interference, with detailed schematics and thorough review processes being crucial for success.