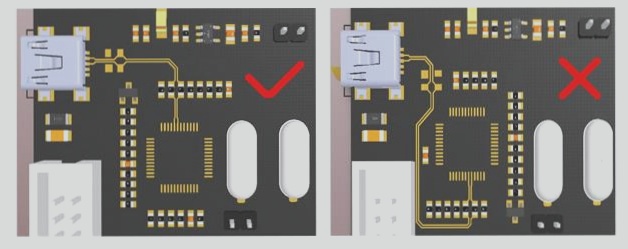
4 Techniques for Multilayer PCB Identification
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in electronic devices, serving as foundational infrastructure for connecting and transmitting electrical signals among electronic components. They are typically composed of materials like fiberglass and copper foil, offering excellent conductivity and mechanical properties. PCB design considerations include circuit connectivity, layout, and thermal management. Effective PCB layouts can minimize electromagnetic interference and signal delay, thereby enhancing overall device reliability and stability. Strict quality control and production processes are vital during PCB manufacturing to ensure high performance and extended product lifespan, ultimately influencing the overall quality and reliability of electronic devices.