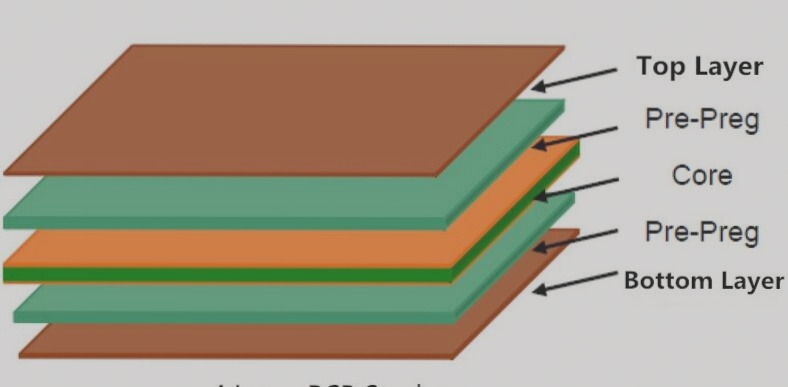
Summary: Ensure rigid circuit board durability and stability through material selection (fiberglass, ceramic), reinforcement materials, hot pressing, multi-layer boards, plate supports, nickel metallization, precise thickness control, consistent substrate and copper foil thickness, soldering temperature regulation, brackets for fixation, manual bending correction, metal foil reinforcement, moisture content control, isolation layers for copper foil, careful installation practices, sensible cabling planning, simplified PCB design, appropriate drilling sizes, reinforced supports, temperature management, compression during manufacturing, robust packaging, and regular inspections.