What is Copper Thieving in PCB? – PCB Knowledge and Basic Information – Wellcircuits
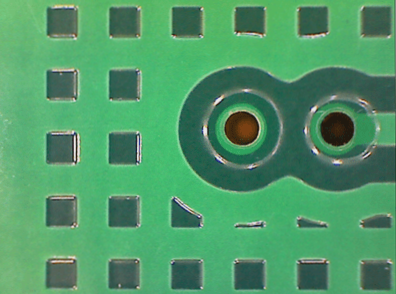
Copper thieving is a technique used to balance the copper distribution on a PCB by adding small copper circles squares or even a solid copper plane to larger blank spaces The added copper is not co
What is Copper Thieving in PCB? – PCB Knowledge and Basic Information – Wellcircuits Read More »