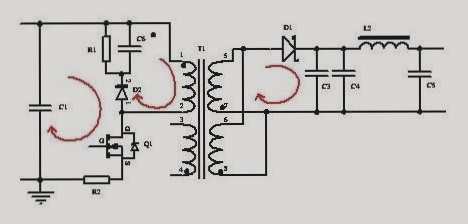
Here’s a refined version of the provided text in English: — 1. **Separation of Digital and Analog Signals**: A fundamental principle in PCB layout is to isolate digital and analog components to prevent interference. High-speed signals should be kept away from low-speed signals, and separate ground planes for digital and analog circuits are crucial to minimize noise. 2. **Power and Ground Wiring Precautions**: – Use decoupling capacitors between power supply lines and ground to filter noise and ensure stable current supply to chips. – Ensure power traces are wider than signal traces, with ground traces wider than power traces. – Utilize large copper areas for ground planes, connecting unused PCB areas to ground in multi-layer boards. 3. **Integration of Digital and Analog Circuits**: – Carefully integrate digital and analog circuits to mitigate ground noise and interference. – Position high-frequency signal lines away from sensitive analog components. – Manage separate digital and analog grounds within the PCB design, except at necessary interface points. 4. **Management of Signal Line Corners**: – Minimize reflections by avoiding right-angle corners in favor of 45-degree angles or rounded corners where appropriate. – Use rounded corners judiciously, especially for sensitive signal paths. 5. **Post-Wiring Design Rule Verification**: – Conduct thorough checks post-design to ensure compliance with production standards and operational requirements. – Verify spacing between wires, components, and through-holes. – Confirm appropriate widths for power and ground traces to maintain low impedance. – Implement special measures for critical signal lines, ensuring short lengths and proper separation of input and output lines. – Check for potential signal short-circuits due to PCB graphics. In conclusion, effective PCB design requires expertise in design tools and software, supported by theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Attention to detail throughout the design process ensures the final PCB meets quality standards and performs optimally. — This revision aims to enhance clarity and readability while maintaining technical accuracy and structure from the original content.