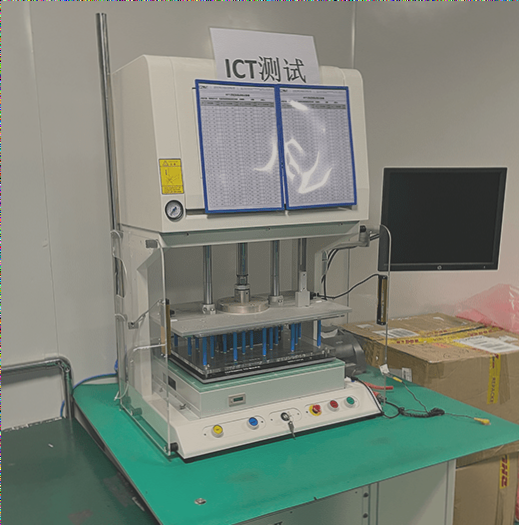
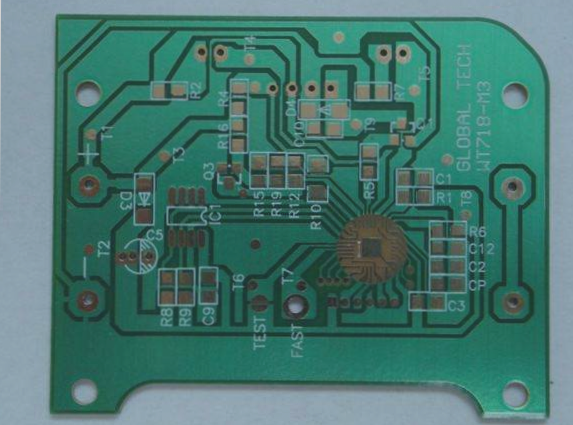
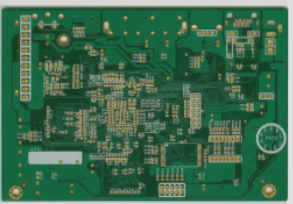
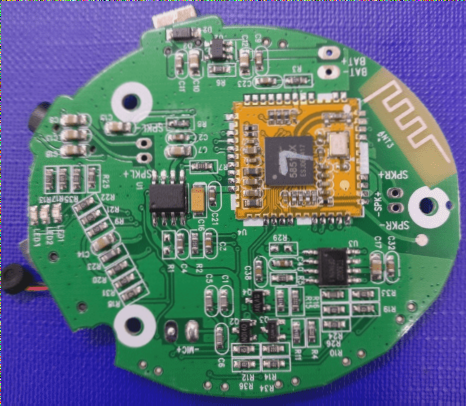
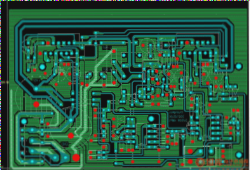
A rigid PCB prototype is a functional sample of a printed circuit board (PCB) created before manufacturing the final product. It serves a critical role in the PCB design process by enabling designers to test and verify their design’s functionality prior to mass production. Prototypes can be developed using methods such as breadboarding, solderless breadboarding, or PCB design software to create a virtual prototype. After creation, the prototype undergoes functional testing, allowing for necessary adjustments before moving to mass production. Rigid PCB prototypes are crucial for saving time and costs by identifying and rectifying design flaws early in the process. PCB manufacturing encompasses designing, fabricating, and assembling PCBs for electronic devices. The process typically involves these steps: Design: PCB manufacturing begins with designing the circuit board using specialized software to create a schematic and layout components and traces on the board. Fabrication: Once the design is complete, the PCB undergoes fabrication. This includes transferring the design onto a copper-clad board and etching to remove unnecessary copper. Drilling: After etching, the board is drilled to create holes for components and vias (connections between PCB layers). Plating: The board is then plated with a thin layer of copper to form conductive traces. Soldermask: A solder mask is applied to protect exposed copper and prevent solder bridges between traces. Silkscreen: A silk screen is applied to label components and indicate polarity on the board. Assembly: The final step involves manually or automatically assembling components onto the board. Overall, PCB manufacturing is a complex process requiring high expertise and precision to ensure the final product’s reliability and functionality.