Summary of PCB White Residue Treatment and Design Considerations
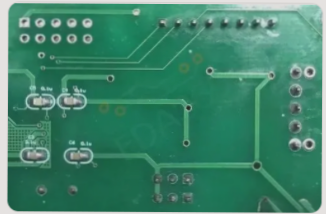
White residues on PCB circuit boards after soldering are typically caused by improper flux usage, solvent degradation, or oxidation, and can be addressed by switching flux types, cleaning with strong solvents, and reducing storage time to maintain both performance and appearance.
Summary of PCB White Residue Treatment and Design Considerations Read More »