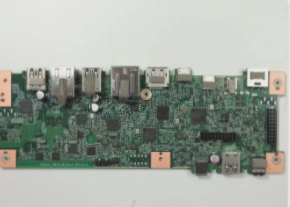
1. Technical Analysis of FPC Flexible Circuit Boards
FPC flexible circuit boards, also known as flexible printed circuit boards or soft boards, are essential components in modern electronics. According to IPC definitions, a flexible printed circuit board is a product that is designed and manufactured on a flexible substrate using printing techniques. FPC flexible circuit boards represent a significant category of circuit boards. Their key characteristics include:
(1) FPC flexible circuit boards are compact and lightweight.
(2) FPC flexible circuit boards are capable of being moved, bent, and twisted.
(3) FPC flexible circuit boards exhibit excellent electrical properties, dielectric performance, and thermal resistance.

(4) FPC flexible circuit boards exhibit high reliability in assembly and operational convenience.
(5) FPC flexible circuit boards can be connected and installed in three different positions.
(6) FPC flexible circuit boards facilitate effective heat dissipation.
(7) Cost-effective.
(8) Consistent processing continuity.
FPC flexible circuit boards are compact and lightweight, significantly minimizing device volume. They are ideal for the development of electronic products aiming for high density, miniaturization, lightweight design, thin profiles, and enhanced reliability. Their exceptional flexibility allows for free bending, winding, twisting, and folding, enabling three-dimensional wiring that can be arranged according to spatial layout requirements. This adaptability supports the integration of component assembly and wire connections.
FPC flexible circuit boards boast excellent electrical properties, high thermal resistance, and flame retardance. They demonstrate stable chemical properties, ensuring reliability. Their high assembly reliability simplifies circuit design, significantly reducing assembly workload. This ease of use helps maintain circuit performance while lowering overall machine costs. Strength can be enhanced by utilizing reinforced materials for added mechanical stability. Additionally, the design of soft-hard combinations compensates for the flexible substrate’s slightly limited load-bearing capacity.
2. Important Considerations in FPC Flexible Circuit Board Production
Due to the unique characteristics of FPC flexible circuit boards, the production process differs from traditional methods. Here are some key precautions to keep in mind during the manufacturing process:
1. Since most flexible circuit boards are made from coiled materials, double-sided FPCs with through-holes cannot utilize the RTR process; hence, materials must be processed in sheet form.
2. Generally, the materials used for flexible circuit boards are quite thin, making them fragile. Extra care should be taken to protect the material during cutting.
3. For small material quantities, hand cutting is required. For larger quantities, automatic slicers should be employed.
4. If the material is pre-cut, use equipment to stack it automatically and neatly, effectively reducing issues such as pressure pits, creases, and wrinkles.
5. When stacking by hand, wear gloves that do not shed fibers, preferably latex, to prevent contamination of the material surface.
6. If cutting copper-clad laminates during processing, be mindful of the rolling direction of the copper.
7. In pre-production design or subsequent processing, the cutting frame should not be used as a positioning reference for further steps.
FPC flexible circuit boards, also known as flexible printed circuit boards or soft boards, are essential components in modern electronics. According to IPC definitions, a flexible printed circuit board is a product that is designed and manufactured on a flexible substrate using printing techniques. FPC flexible circuit boards represent a significant category of circuit boards. Their key characteristics include:
(1) FPC flexible circuit boards are compact and lightweight.
(2) FPC flexible circuit boards are capable of being moved, bent, and twisted.
(3) FPC flexible circuit boards exhibit excellent electrical properties, dielectric performance, and thermal resistance.

(4) FPC flexible circuit boards exhibit high reliability in assembly and operational convenience.
(5) FPC flexible circuit boards can be connected and installed in three different positions.
(6) FPC flexible circuit boards facilitate effective heat dissipation.
(7) Cost-effective.
(8) Consistent processing continuity.
FPC flexible circuit boards are compact and lightweight, significantly minimizing device volume. They are ideal for the development of electronic products aiming for high density, miniaturization, lightweight design, thin profiles, and enhanced reliability. Their exceptional flexibility allows for free bending, winding, twisting, and folding, enabling three-dimensional wiring that can be arranged according to spatial layout requirements. This adaptability supports the integration of component assembly and wire connections.
FPC flexible circuit boards boast excellent electrical properties, high thermal resistance, and flame retardance. They demonstrate stable chemical properties, ensuring reliability. Their high assembly reliability simplifies circuit design, significantly reducing assembly workload. This ease of use helps maintain circuit performance while lowering overall machine costs. Strength can be enhanced by utilizing reinforced materials for added mechanical stability. Additionally, the design of soft-hard combinations compensates for the flexible substrate’s slightly limited load-bearing capacity.
2. Important Considerations in FPC Flexible Circuit Board Production
Due to the unique characteristics of FPC flexible circuit boards, the production process differs from traditional methods. Here are some key precautions to keep in mind during the manufacturing process:
1. Since most flexible circuit boards are made from coiled materials, double-sided FPCs with through-holes cannot utilize the RTR process; hence, materials must be processed in sheet form.
2. Generally, the materials used for flexible circuit boards are quite thin, making them fragile. Extra care should be taken to protect the material during cutting.
3. For small material quantities, hand cutting is required. For larger quantities, automatic slicers should be employed.
4. If the material is pre-cut, use equipment to stack it automatically and neatly, effectively reducing issues such as pressure pits, creases, and wrinkles.
5. When stacking by hand, wear gloves that do not shed fibers, preferably latex, to prevent contamination of the material surface.
6. If cutting copper-clad laminates during processing, be mindful of the rolling direction of the copper.
7. In pre-production design or subsequent processing, the cutting frame should not be used as a positioning reference for further steps.