Precision Control Techniques for PCB Board Milling
- High-quality outcomes in PCB board milling rely on precision control techniques and methods.
- The milling process demands meticulous attention to detail for accurate dimensions and surface finishes.
- Key techniques like feed rate adjustments and spindle speed optimization are crucial for precision control.
- Advanced CNC machinery significantly enhances milling precision.
- Proper tooling strategies are essential for achieving desired tolerances.
- Real-time monitoring of milling parameters aids in early issue identification.
- Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and equipment longevity.
- Continuous improvement and method adaptation are vital to meet industry standards.
- Staying updated with the latest innovations is critical for PCB manufacturing success.
Accuracy Control Techniques for PCB Milling
- Choice of cutting direction, compensation methods, positioning techniques, frame structure, and cutting points are critical factors for milling precision.
Cutting Direction and Compensation Method
When milling PCBs, the cutting direction and compensation method play a crucial role in achieving dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces.
- Utilize counterclockwise cutting for external contours and forward milling for frames or grooves.
- Milling plate compensation ensures the milling shape aligns with programmed settings.
Positioning Method and Cutting Point
Effective positioning methods are essential for precision in PCB milling.
- Internal positioning using non-metallic holes as reference points enhances accuracy.
- External positioning simplifies production but requires caution to prevent board damage.
The Latest in PCB Manufacturing Techniques
When it comes to PCB manufacturing, staying updated on the latest techniques is crucial. Here are some cutting-edge methods that are revolutionizing the industry:
1. Segmented Milling Method
- The segmented milling method is a game-changer in PCB production. It involves milling the plate, pausing the program, securing the board with adhesive tape, and drilling out joint points with precision.
- This method reduces costs, simplifies management, and eliminates the need for installation or positioning holes. It optimizes substrate utilization and streamlines early production processes.
- However, it’s important to note that the use of drill bits can sometimes result in protrusions on the circuit board shape, which may not meet aesthetic standards and could lead to longer milling times.
2. Frame and Cutting Point
Frame design plays a crucial role in PCB production. A well-designed frame ensures electroplating uniformity and smooth milling processes. On the other hand, poor design can cause frame deformation, waste blocks, and damage to milling cutters.
Choosing the right cutting points and processing sequences is vital to maintain frame strength and speed. Incorrect choices may result in deformation and scrap of the printed board.
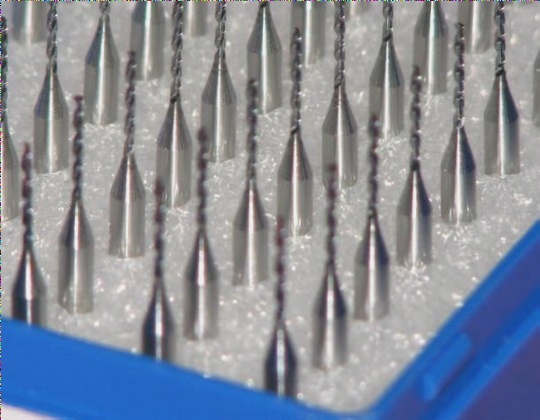
3. Process Parameters of Milling
When it comes to milling the shape of printed circuit boards, using a cemented carbide milling cutter is standard practice. The cutting speeds typically range from 180 to 270 m/min.
Here is a formula for reference:
- S = pdn/1000 (m/min)
Where:
- P: π (3.1415927)
- d: Diameter of the milling cutter in mm
- n: Speed of the milling cutter in RPM