The Importance of PCB Design in Enhancing Thermal Performance
- Customized IC devices require close collaboration between system designers and manufacturers to meet cooling requirements.
- Physical spacing and positioning of high power consumption components on the PCB are crucial for heat conduction.
- Isolating temperature-sensitive components from high power components is essential for optimal performance.
- Maximizing copper content in the PCB enhances thermal performance of system components.
- Utilizing wider wires and strategic wiring placement aids in heat dissipation.
For better heat dissipation, consider the top and bottom layers of the PCB as prime locations. Using wider wires and positioning wiring away from high power consumption devices can provide a path for heat dissipation. One excellent method for PCB heat dissipation is the use of a special heat conduction plate, which is typically located on the top or back of the PCB and is thermally connected to the device through direct copper connection or thermal through-hole.
In the case of inline packaging (with leads on both sides), the heat conduction plate can be located on the top of the PCB and its shape can resemble a “dog bone” (with a small area in the middle, as small as the package, and a large copper area connected far from the package at the two ends). For four side packaging (with leads on all four sides), the heat transfer plate must be located at the back of the PCB or within the PCB.
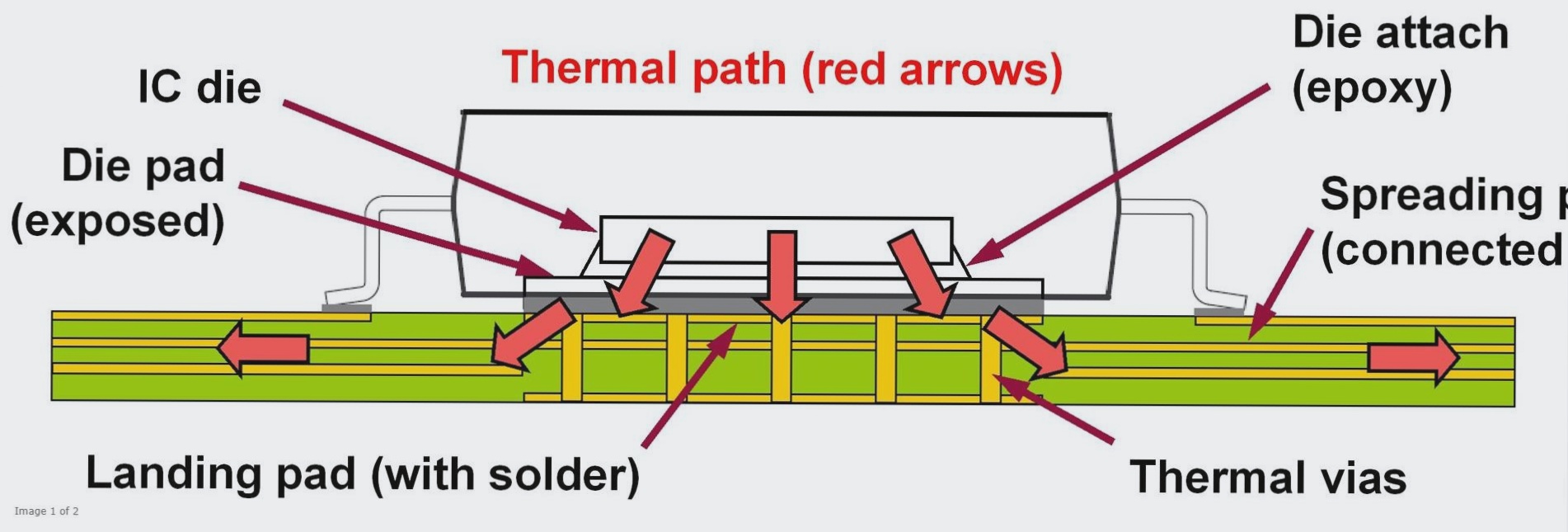
Figure 3 provides an example of the “dog bone” method for a dual in-line package.
Improving Thermal Performance in PowerPad Packaging
Enhancing the thermal performance of PowerPad packaging can be achieved by increasing the size of the heat conducting plate. The size of the heat conducting plate plays a crucial role in improving thermal efficiency. While product data sheets typically provide dimensions in tables, quantifying the impact of additional copper on customized PCBs can be challenging. Online calculators now allow users to select a device and adjust the size of the copper pad to estimate its effect on the thermal performance of non-JEDEC PCBs. These tools emphasize how PCB design influences heat dissipation.
- For a four-side package, the top pad area should be slightly smaller than the bare pad area of the device. Burying or positioning the pad on the back layer is a primary method to enhance cooling.
- In the case of a dual in-line package, the “dog bone” pad style can be utilized for heat dissipation.
Enhanced Cooling Strategies
Systems with larger PCBs can aid in cooling. By connecting screw heat dissipation to the heat conduction plate and the ground plane, the screws used for PCB installation can serve as effective heat paths to the system base. However, the number of screws should be chosen carefully to balance heat conduction and cost effectively.
- Attaching a metal PCB reinforcement plate to the heat conduction plate can expand the cooling area.
- In scenarios where the PCB cover is housed, utilizing type-controlled welding repair material can offer superior thermal performance compared to air-cooled housing.
Optimizing Cooling Solutions
Cooling solutions like fans and heat sinks are common methods for system cooling, but they may require more space or design modifications to maximize effectiveness.
Maximizing Thermal Performance
Designing a system with high thermal performance goes beyond selecting quality IC devices and closed solutions. The thermal efficiency of IC devices relies on the PCB’s capacity and the thermal system that facilitates rapid cooling. Passive cooling techniques can significantly enhance system heat dissipation.