1. The FPC public equipment & Use of high-end soft plate
2. Soft laminate is a highly reliable flexible printed circuit board made of polyimide or polyester film as a substrate.
3. Soft plate or FPC for short, features high distribution density, lightweight, and thin design.
4. Flexible PCB is a highly reliable, flexible printed circuit board made of polyimide or polyester film as a substrate.
5. Soft plate or FPC for short, features high distribution density, lightweight, and thin design.
6. Mainly used in mobile phones, laptops, PDAs, digital cameras, LCDs, and many other products.

1. A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is primarily composed of solder pads, through-holes, mounting holes, traces, components, connectors, fillers, and electrical boundaries. The main functions of each component are as follows:
2. Solder pads: Metal holes used for soldering component pins.
3. Through-holes: Metal holes used to interconnect component pins between layers.
4. Mounting holes: Used for securing the PCB.
5. Traces: Copper conductive pathways used to connect component pins.
6. Connectors: Components facilitating connections between PCBs.
7. Fillers: Copper coatings used in ground networks to reduce impedance effectively.
8. Electrical boundaries: Used to define the PCB’s size; all components should not exceed this boundary.
9. The functions of flexible PCBs can be categorized into four types: Lead Line, Printed Circuit, Connector, and Integration of Function. Applications span across computers, peripheral systems, consumer electronics, and automotive industries.
10. Soft light stripe classification: Based on the combination of base material and copper foil, flexible PCBs are divided into two types: those with adhesive and those without. Adhesive-free flexible PCBs generally command a higher price due to superior flexibility, bonding strength between copper foil and base material, and flatness of solder pads. They are typically reserved for demanding applications like COF (CHIP ON FLEX, where the chip is mounted on the flexible board with high flatness requirements). However, due to their elevated cost, adhesive-free flexible PCBs are not widely used in the market. Most flexible PCBs in the market employ adhesive. Since flexible PCBs are primarily utilized in bending scenarios, improper design or processing may lead to micro-cracks and soldering defects.
11. For relatively simple circuit designs with moderate volume and suitable space, traditional interconnect methods are more cost-effective. Flexible circuits are advantageous for complex circuits, extensive signal handling, or specialized electrical/mechanical requirements. Flexible assembly becomes economical when the application’s size and performance exceed the capabilities of rigid circuits.
12. A 12MIL pad with a 5mil through-hole and a 3mil line and spacing flexible circuit can be produced on a single film, making it more reliable to mount chips directly onto the film. Additionally, flexible materials eliminate the need for connectors, resulting in cost savings compared to rigid materials. Flexible films are also free of flame retardants, reducing contamination risks from ion drills. These films may offer protective properties and solidify at higher temperatures, leading to increased vitrification temperatures.
2. Soft laminate is a highly reliable flexible printed circuit board made of polyimide or polyester film as a substrate.
3. Soft plate or FPC for short, features high distribution density, lightweight, and thin design.
4. Flexible PCB is a highly reliable, flexible printed circuit board made of polyimide or polyester film as a substrate.
5. Soft plate or FPC for short, features high distribution density, lightweight, and thin design.
6. Mainly used in mobile phones, laptops, PDAs, digital cameras, LCDs, and many other products.
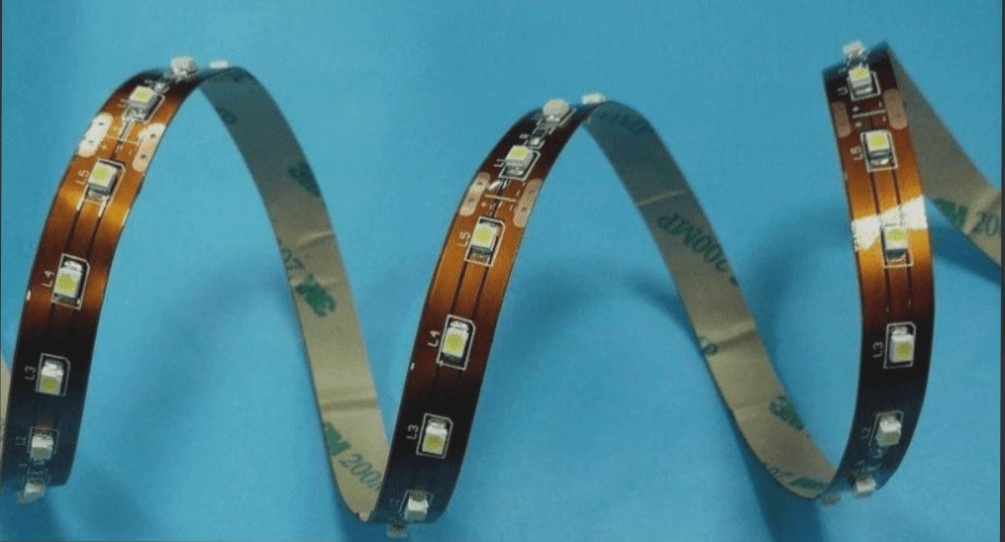

1. A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is primarily composed of solder pads, through-holes, mounting holes, traces, components, connectors, fillers, and electrical boundaries. The main functions of each component are as follows:
2. Solder pads: Metal holes used for soldering component pins.
3. Through-holes: Metal holes used to interconnect component pins between layers.
4. Mounting holes: Used for securing the PCB.
5. Traces: Copper conductive pathways used to connect component pins.
6. Connectors: Components facilitating connections between PCBs.
7. Fillers: Copper coatings used in ground networks to reduce impedance effectively.
8. Electrical boundaries: Used to define the PCB’s size; all components should not exceed this boundary.
9. The functions of flexible PCBs can be categorized into four types: Lead Line, Printed Circuit, Connector, and Integration of Function. Applications span across computers, peripheral systems, consumer electronics, and automotive industries.
10. Soft light stripe classification: Based on the combination of base material and copper foil, flexible PCBs are divided into two types: those with adhesive and those without. Adhesive-free flexible PCBs generally command a higher price due to superior flexibility, bonding strength between copper foil and base material, and flatness of solder pads. They are typically reserved for demanding applications like COF (CHIP ON FLEX, where the chip is mounted on the flexible board with high flatness requirements). However, due to their elevated cost, adhesive-free flexible PCBs are not widely used in the market. Most flexible PCBs in the market employ adhesive. Since flexible PCBs are primarily utilized in bending scenarios, improper design or processing may lead to micro-cracks and soldering defects.
11. For relatively simple circuit designs with moderate volume and suitable space, traditional interconnect methods are more cost-effective. Flexible circuits are advantageous for complex circuits, extensive signal handling, or specialized electrical/mechanical requirements. Flexible assembly becomes economical when the application’s size and performance exceed the capabilities of rigid circuits.
12. A 12MIL pad with a 5mil through-hole and a 3mil line and spacing flexible circuit can be produced on a single film, making it more reliable to mount chips directly onto the film. Additionally, flexible materials eliminate the need for connectors, resulting in cost savings compared to rigid materials. Flexible films are also free of flame retardants, reducing contamination risks from ion drills. These films may offer protective properties and solidify at higher temperatures, leading to increased vitrification temperatures.