PCB Copy Board
PCB Copy Board, also known as circuit board copying or PCB reverse engineering, involves the process of analyzing and reconstructing a circuit board’s design files, schematic diagrams, and technical documents. This allows for the replication of the original PCB template.
Reasonably Divide Functional Areas
When reverse designing a PCB schematic, dividing functional areas thoughtfully can enhance drawing efficiency. Grouping components with similar functions together simplifies the reconstruction process.

Understanding the Division of Functional Areas
Understanding electronic circuit principles is crucial for dividing functional areas effectively. Identifying core components and utilizing PCB component serial numbers can expedite the process.
Select Appropriate Reference Components
Choosing key components as reference points during schematic design ensures accuracy. Integrated circuits, transformers, and transistors are examples of suitable reference parts.
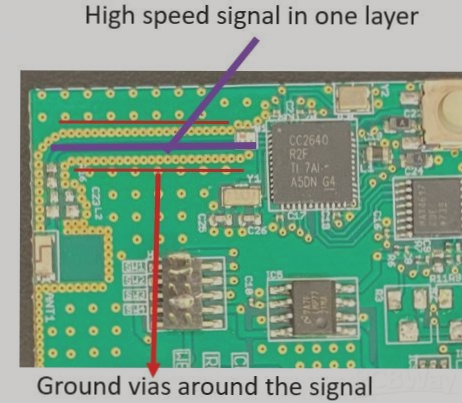
Correctly Identify and Route Wiring
Differentiating between ground, power, and signal lines requires a good understanding of power supply design and PCB routing techniques. Using grounding symbols and color-coded lines can aid in clear identification.
Understand the Basic Framework and Learn from Similar Schematics
Having knowledge of electronic circuit structures and schematic diagramming techniques is essential. Learning from existing circuit diagrams can help in designing schematics for new products.
Verification and Optimization
After completing the schematic, thorough testing and validation are necessary. Components’ nominal values must be accurate, and the schematic should be compared against the PCB file diagram for a perfect match.
These key points are crucial when reverse-engineering a PCB schematic diagram.