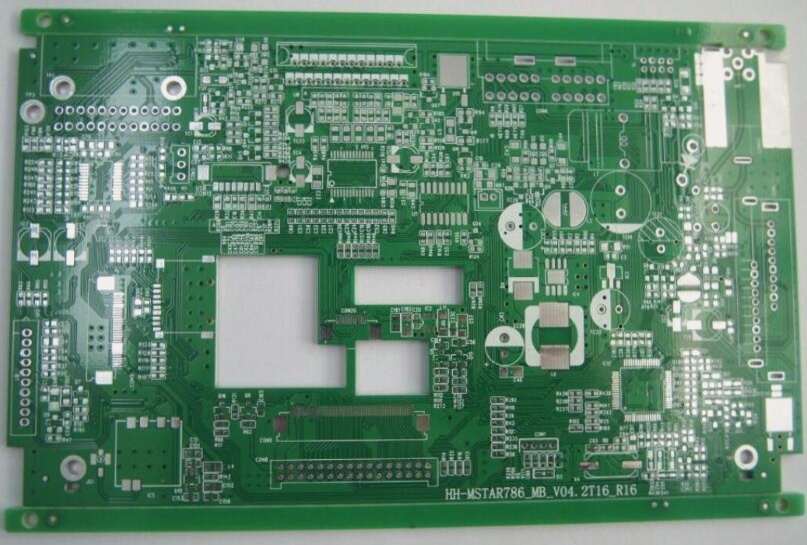
Copper Electroplating in PCB Fabrication
Copper electroplating is crucial in PCB fabrication, serving as a pre-plating layer to enhance coating adhesion in the copper/nickel/chromium system. It provides protection, decoration, and improves adhesion and corrosion resistance between layers. Additionally, it is used for local anti-carburization, metallizing printed board holes, and as a surface layer of printing rollers. Chemically treated colored copper layers coated with organic film can also be utilized for decorative purposes.
Common Issues in Acid Copper Electroplating
- Rough Electroplating
- Copper Particles on Plate Surface
- Electroplating Pits
- Whitening or Uneven Coloration
Solutions for Rough Plating
Rough board edges can result from excessive electroplating current. To address this, reduce the current and check for abnormalities using a card meter. Roughness on the entire board is rare but may occur in specific cases and requires thorough examination.
Tomorrow’s Weather Impact
Tomorrow, the winter temperature will be low, which may affect the brightener content in the plating process. Insufficient brightener content or improper cleaning of reworked faded sheets can lead to similar rough plating issues.
Plate Surface Copper Particles
Copper Particles on PCB Surface
- Copper particles on the board surface can result from various factors in the manufacturing process.
- Issues with copper immersion can lead to particle contamination.
- Roughness caused by alkaline degreasing and drilling dust can contribute to surface imperfections.
- Quality failures may occur due to poor microetching agents or impurities in chemicals.
- Activation solution problems can stem from pollution or maintenance issues.
- Excessive copper content or low temperatures in the micro-etching tank can lead to quality issues.
- Proper process adjustments and tank maintenance are essential to prevent copper particle contamination.
Electroplating Pits
- Pits in electroplating can arise from various processes, including copper immersion and pattern transfer.
- Contamination during microetching can lead to pits in the PCB surface.
- Equipment maintenance and cleaning issues can cause pits during the graphics transfer process.
- Pre-treatment processes for electroplating can result in turbid solutions and surface pollution.
- Non-conductive particles from poor encapsulation can cause electroplating pits.
Whitish or Uneven PCB Surface Color
- Issues in the acid copper electroplating tank can lead to whitish or uneven surface colors.
- Air bubbles from misaligned tubes or leaks in the filter pump can adhere to the PCB surface.
- Contaminated cotton cores can affect the bath solution and cause plating defects.
- Proper aeration and foam removal are essential for maintaining a consistent surface color.
- Polishing, maintenance, and cleaning problems can also contribute to surface discoloration.