What is a Flexible PCB?
Flexible printed circuits (FPC) are innovative, versatile components made with flexible substrates. These are typically created using polyimide materials and one to several layers of copper, making them capable of bending without breaking.
FPCs are used in a wide range of applications, from connectors to full circuits that include assembled components. They also can withstand soldering heat, making them suitable for high-temperature environments. Compared to rigid boards, flexible PCBs offer enhanced durability, particularly when exposed to thermal stress.
One of the standout features of FPCs is their ability to bend and twist, enabling greater design flexibility in compact or challenging spaces.
What are the Differences Between Flex and Rigid PCBs?
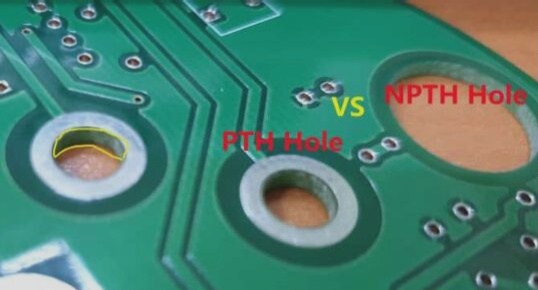
1. Material
Rigid PCBs are usually made of FR4 (glass-epoxy composites), whereas flexible PCBs are primarily made from polyimide, a flexible material that allows bending without damage. While polyimide can sometimes be used in rigid boards, it’s not as common.
2. Coverlay
Flex PCBs often use a flexible coverlay or mask, while rigid boards rely on a solder mask for protection. A flexible coverlay is either routed or laser cut to form openings and is attached using an adhesive layer. Rigid boards don’t require a coverlay, just a solder mask.
3. Stiffeners
In flex PCBs, stiffeners made of materials like FR4, aluminum (Al), stainless steel (SUS), or polyimide are used to reinforce specific areas that need to remain rigid. These stiffeners can be laminated or adhered using pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA). Rigid PCBs, on the other hand, do not require additional stiffening.
4. Permittivity
The dielectric constant (relative permittivity) varies greatly across materials used in rigid boards. In contrast, flexible PCBs made of polyimide typically have a permittivity of 3.4, ensuring consistent performance even under varying conditions.
What are the Benefits of Flex PCBs?
Flexible PCBs offer several distinct advantages that make them an ideal choice for many applications:
- Space-Saving Design: Flexible PCBs can be bent and shaped to fit into tight spaces, making them ideal for compact electronic devices.
- Reduced Weight: Their flexibility and lighter material reduce the overall weight of the final product, which is particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace or mobile electronics.
- Durability: Flex PCBs are resistant to vibrations and thermal stresses, which increases the longevity of electronic components in harsh environments.
- Improved Reliability: With fewer connections and joints, flex circuits reduce the chances of failure due to physical stress or wear.
- Design Flexibility: Their ability to bend and conform to 3D shapes opens up new possibilities for product design, especially in wearable technology and medical devices.
Key Features of Flex Circuits
1. Lightweight
One of the most notable advantages of flex circuits is their lightweight design. Flex circuits use polyimide material, which is significantly lighter than traditional FR4 (fiber-reinforced epoxy). This makes them ideal for applications where minimizing weight is crucial, such as in aerospace, medical devices, and portable electronics.
2. Thin Profile
Flex circuits are known for their thin profile. A typical 2-layer flex circuit can range in thickness from just 4.4 mils to 10 mils. This thinness allows for compact and space-efficient designs, which are essential in modern electronic devices where saving space is critical. The thinner the flex circuit, the more versatile it becomes for fitting into small or irregularly shaped enclosures.
3. Flexible and Durable
As the name suggests, flex circuits are incredibly flexible. They can be bent and twisted to fit the design requirements, offering more freedom to reduce the overall mechanical footprint of the system. This flexibility allows engineers to create more intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible with traditional rigid circuit boards.
4. High Temperature Resistance
Polyimide flex materials offer superior performance in high-temperature environments. Compared to FR4, polyimide-based flex circuits can withstand much higher temperatures without losing their mechanical and electrical properties. Additionally, these materials are resistant to oils, gases, and acids, making them suitable for harsh industrial and automotive applications.
Applications of Flex Circuits
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices
- Medical Devices: Sensors, monitors, and diagnostic equipment
- Automotive: Electronic control units and sensors
- Aerospace: Satellite systems and aircraft electronics
- Industrial: Robotics, automation systems, and power equipment
Why Choose Well Circuits?
Flex circuits offer several key benefits over traditional rigid boards, including:
- Space-saving design for compact products
- Increased durability and resistance to fatigue
- Ability to perform in high-temperature environments
- Improved flexibility for complex and intricate designs
Whether you are designing for consumer electronics, automotive systems, or industrial machinery, flex PCBs provide unparalleled flexibility and reliability. Their lightweight and thin profile make them an excellent choice for many applications requiring high-performance circuits that can withstand extreme conditions.