Ceramic PCB Boards vs. Ordinary PCB Boards: A Comprehensive Comparison
Introduction
Ceramic PCB boards are specialized boards known for their exceptional thermal conductivity, insulation properties, and high dielectric constant. They are particularly well-suited for applications that require efficient heat dissipation. In contrast, ordinary PCB boards have their own set of advantages and are commonly used in various commercial products.
Key Differences
- Materials: Ceramic PCB boards utilize inorganic materials like aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride, while ordinary PCB boards use organic materials such as FR4 glass fiber boards.
- Performance and Applications: Ceramic PCB boards are ideal for industries with high heat dissipation needs like high-power LED lighting and high-frequency communications. On the other hand, ordinary PCB boards are versatile and widely used in civilian commercial products.
Additional Insights
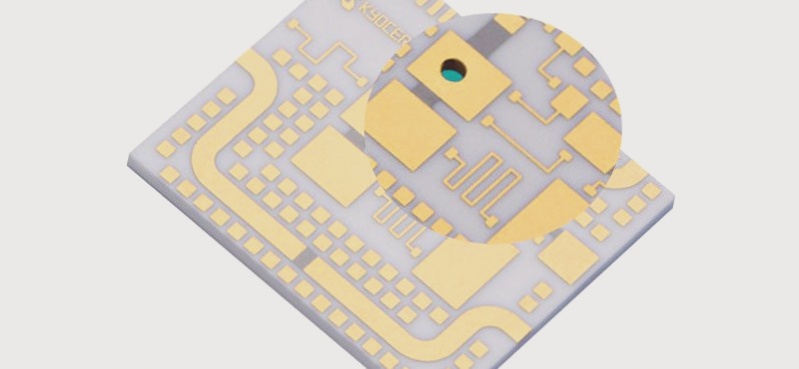
- Materials and Applications: Ceramic PCB boards are commonly used in refrigeration chips, automotive electronics, and high-power modules, emphasizing the importance of heat dissipation. High-frequency boards, on the other hand, are prevalent in high-frequency communications and aerospace industries.
- Combined Applications: In specific high-frequency communication scenarios requiring efficient heat dissipation, a combination of ceramic PCB boards and high-frequency boards is often necessary, resulting in high-frequency ceramic PCB boards.

Quality Assurance Tips
- Inspect Ceramic Substrate Quality Parameters: Ensure the selected ceramic substrate offers chemical stability, high thermal conductivity, and resistance to extreme conditions.
- Examine Craftsmanship: Check for precise spacing between components, tight bonding, and overall flatness to ensure high-quality ceramic substrates.
- Conduct Trials: Test the thermal conductivity by monitoring temperature and current flow to identify any issues with heat dissipation.
- Research Manufacturers: Choose reputable manufacturers with a history of quality production and positive user feedback to ensure the reliability of ceramic substrates.