Advancements in PCB Testing Methods
Introduction
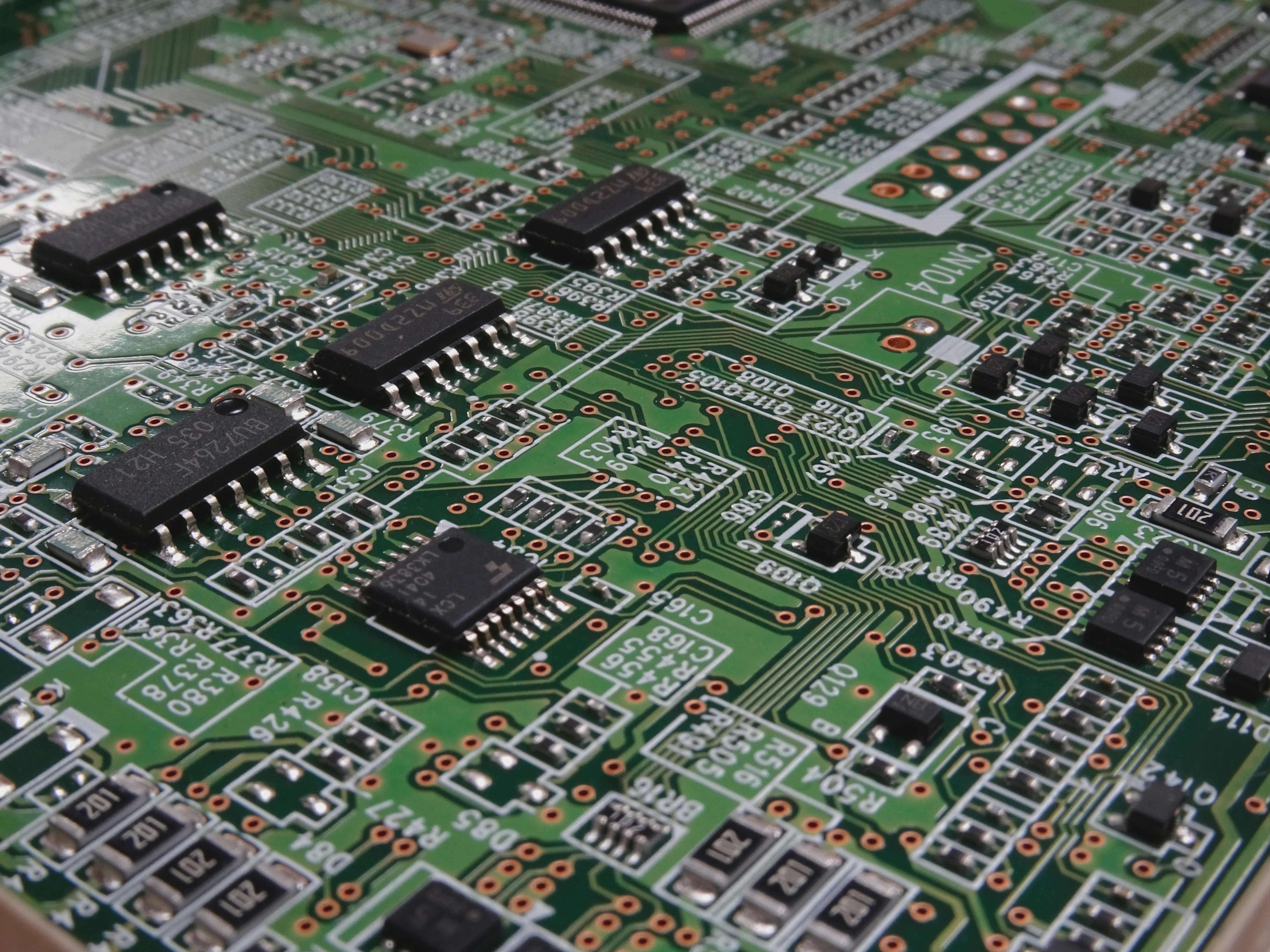
With the rise of surface mount technology, the packaging density of PCB multilayer boards has significantly increased. This has led to the importance of automatic inspection methods for PCB multilayer films, even for boards with lower density or average production volumes.
Needle Bed Test Method
The needle bed test method involves spring-loaded probes connected to each inspection point on the PCB. These probes apply consistent pressure and are arranged in a configuration known as a “needle bed.” Testing software controls the test points and signals, allowing for simultaneous testing of both sides of the PCB. However, this method requires all test points to be located on the solder side during design.

General-Purpose Grid Processor
A general-purpose grid processor consists of a drill plate and pins with various pitches. These pins act as probes and are connected to the PCB multilayer board. Continuity detection is performed by accessing the endpoints of the grid, ensuring thorough testing of every network on the PCB.
Double Probe or Flying Probe Test Method
The flying probe test method utilizes probes mounted on a micro-head that moves freely on the X-Y plane. Test points are determined by CAD Gerber data, allowing for precise testing without restrictions on probe movement. This method is ideal for manufacturers of complex PCBs with lower yields.
Bare Board Testing for PCBs
When it comes to testing PCBs, there are different approaches you can take. While specialized instruments exist for this purpose, using general-purpose instruments can be a more cost-effective solution in the long run.
For boards with pin components and surface-mount devices, a standard grid size of 2.5 mm is typically used. It is recommended that the test pad size should be at least 1.3 mm for this grid. For Integrated Module Mounting (IMM) grids, the test pad size should be larger than 0.7 mm to ensure proper testing.
Combining a universal tester with a flying probe tester can offer accurate and cost-effective testing for high-density PCBs. Additionally, using a conductive rubber tester can help detect any deviations from the grid, although obstacles like varying cushion block heights after hot air leveling should be considered.
Levels of Testing:
- Bare board inspection
- Online testing
- Functional testing
If you have any questions about PCB testing, feel free to reach out to us at info@wellcircuits.com.