1. Printed circuit boards (HDI boards) are structural components made from insulating materials enhanced with conductor wiring. Once the final product is completed, it incorporates integrated circuits, transistors, diodes, passive components (such as resistors, capacitors, connectors, etc.), and various other electronic elements. Through these connections, electronic signals can be transmitted, enabling the desired functionalities. Thus, the printed circuit board serves as a platform for component interconnections and a base for the mounted parts.
2. As printed circuit boards are not typical end products, their nomenclature can be somewhat misleading. For instance, the motherboard of a personal computer is referred to as a motherboard and cannot simply be termed a circuit board. While circuit boards are present within the motherboard, they are not identical; hence, in industry evaluations, the two are related but not interchangeable. Another example: because integrated circuit components are mounted on circuit boards, the media may refer to them as IC boards, but this designation is not equivalent to printed circuit boards.
3. In the context of increasingly multifunctional and complex electronic products, the spacing between integrated circuit components has decreased, resulting in higher signal transmission speeds. This evolution has led to an increase in wiring density and lengths between connection points. To optimize performance, high-density circuit configurations and micro-via technologies are essential. Given that single and double-layer boards face challenges in wiring and jumper connections, multilayer circuit boards have become prevalent. Additionally, as the number of signal lines continues to rise, the inclusion of more power and grounding layers has become a vital design consideration, making multilayer PCBs increasingly common.

1. For the electrical demands of high-speed signals, the circuit board must ensure impedance control with alternating current characteristics, high-frequency transmission capabilities, and minimize unnecessary radiation (EMI).
2. Utilizing Stripline and Microstrip structures, a multi-layer design becomes essential.
3. To mitigate quality issues in signal transmission, insulating materials with low dielectric constants and low attenuation rates are employed.
4. To accommodate the miniaturization and arraying of electronic components, the density of circuit boards is continuously increased to meet market demands.
5. The introduction of assembly methods like BGA, CSP, and DCA has pushed printed circuit boards to unprecedented levels of density.
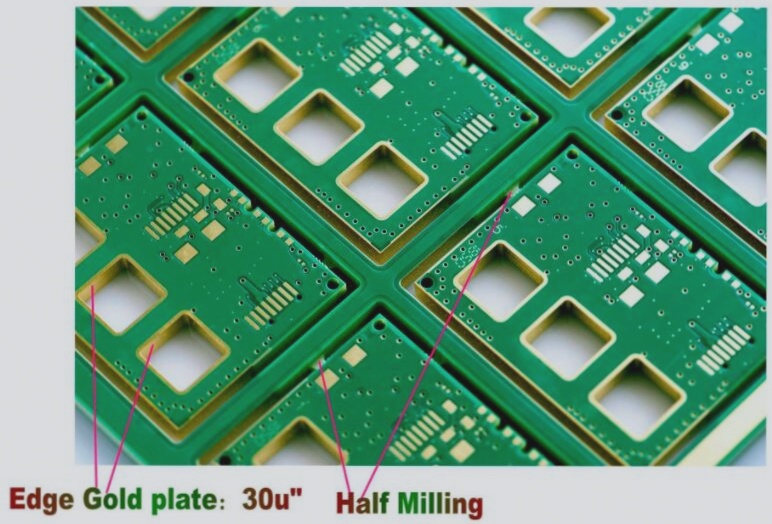
6. Holes with a diameter of less than 150 micrometers are referred to as micro-holes in the industry.
7. Circuit boards utilizing this micro-hole geometric structure technology can enhance assembly efficiency and space utilization, making it essential for the miniaturization of electronic products.
8. Within the industry, there are various names for circuit board products of this structure.
9. For instance, European and American companies have historically used sequential construction methods for their designs, leading to this product being referred to as SBU (sequence build-up process), commonly translated as “sequence build-up process.”
10. In contrast, the Japanese industry labels the pore structure produced by these products as MVP (micro via process), which translates to “micro via process.”
11. Some refer to this type of circuit board as BUM (build-up multilayer board), while traditional multilayer boards are called MLB (multilayer board), generally translated as “build-up multilayer board.”
12. To avoid confusion, the IPC Circuit Board Association in the United States proposed a general term for this product: HDI (high-density interconnection technology), which translates directly to high-density connection technology.
13. However, this terminology does not adequately reflect the characteristics of the circuit board, so the majority of the circuit board industry refers to these products as HDI boards or by the full term “High Density Interconnection Technology.”
14. Nonetheless, due to verbal convenience, some simply refer to such products as high-density PCBs or HDI boards.