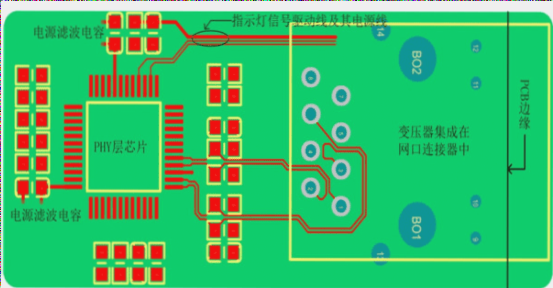
Understanding Backplane PCBs
A backplane PCB, or printed circuit board, acts as a central hub that connects various electronic devices within a system, enabling seamless communication and data exchange.

Figure 1: Backplane PCB
Essentially, a backplane PCB features connectors, slots, and sockets that allow the insertion of different modules like CPUs, memory units, and input/output cards. These components work together, powered by the backplane, to ensure efficient data flow and connectivity.
- Simplified Connectivity: Backplane PCBs streamline the interconnection process, reducing the need for excessive cables and connectors. This simplicity enhances system reliability and minimizes signal loss.
- Scalability: With multiple slots and connectors, backplane PCBs support system expansion and upgrades without extensive modifications, offering a cost-effective solution for future enhancements.
- Enhanced Signal Integrity: These PCBs create a stable environment for signal transmission, reducing the risk of distortion, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference, thus optimizing system performance.
- Space Efficiency: By eliminating bulky cabling, backplane PCBs save space, making them ideal for compact systems or portable devices.
Backplane PCBs find extensive use in servers, routers, telecommunications gear, industrial controls, and medical devices due to their versatility and reliability. Their design varies based on specific system needs, often incorporating multiple copper layers for efficient data transfer and power distribution.
If you seek further information on PCBs or PCBA, reach out to us at info@wellcircuits.com.