Understanding Coverlay in Flex PCBs
A flex PCB, constructed from a flexible substrate, is crucial for applications requiring bending or limited space constraints. Coverlay, a key material in the manufacturing process of flex PCBs, plays a vital role in protecting and insulating circuit components.
Exploring the Role of Coverlay
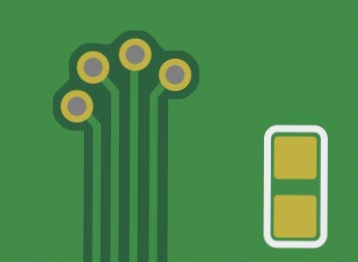
Coverlay, composed of a polyimide substrate and adhesive, encapsulates the exposed circuit layers of a Flex PCB. It safeguards circuit components from mechanical damage, dust, and chemicals, ensuring the board’s reliability during bending and movement.
Key Functions of Coverlay:
- Protection: Shields circuit components from external elements, maintaining reliability.
- Insulation: Prevents electrical current flow between layers, avoiding short circuits.
- Flexibility: Maintains the board’s flexibility and bending capabilities for diverse applications.
Applying the right coverlay material and process is critical for the performance and reliability of flex PCBs.
Choosing the Ideal Coverlay for Your Flex PCB
Factors to consider when selecting coverlay:
- Bending Radius Requirements: Thinner coverlay for strict bending needs.
- Copper Thickness: Adequate adhesive thickness based on finished copper ounces.
- Dielectric Withstand Voltage and Cost considerations.
Differentiating Coverlay and Soldermask
Coverlay vs. Soldermask for Flex PCBs:
- Material: Coverlay uses adhesive and Kapton, while soldermask is liquid-based.
- Dam Size: Coverlay requires a minimum 10 mil dam, soldermask can have a 4 mil dam.
- Trace Width: Coverlay allows 3 mil openings, while soldermask should maintain at least 4 mil openings.
Application Areas:
- PCB Usage: Coverlay is commonly applied on the flexible parts of PCBs, while soldermask is used on the rigid areas. For rigid-flex PCBs with coverlay throughout, ensure appropriate tented or windowed openings.
Component Spacing:
- Pin Spacing: Coverlay may not be suitable for components with very small pin spacing, whereas soldermask can handle finer details effectively.
If you have any inquiries regarding PCBs or PCBA, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us at info@wellcircuits.com.