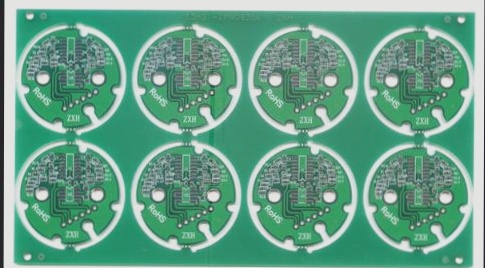
PCB panelization is a manufacturing technique that involves arranging multiple PCBs on a single, larger panel. This method simplifies the movement of the PCBs through the assembly line. Each board in the panel can have the same or a different design. After manufacturing, the panel can be easily separated into individual boards. Panelization is widely used to improve efficiency in the production of small or irregularly shaped PCBs. For PCBs smaller than 50mm x 50mm, panelization is highly recommended.

Figure 1: PCB Panelization
Depanelization Methods
Depanelization refers to the process of separating individual circuit boards from a PCB panel. This can be done using various methods:
V-Scoring
V-scoring is a technique where a V-shaped groove is cut into the panel to separate the individual boards. The size of the groove is a critical factor, especially the “remaining thickness,” which is the thickness of the material left between the two inverted V-shaped grooves. Typically, the recommended remaining thickness is 1/3 of the board’s total thickness.
However, since V-scores must follow straight lines, this method has certain limitations. Panels with irregular shapes or complex cutouts may not be suitable for V-scoring. Additionally, this method is not recommended if components extend over the edge of the board, as they could be damaged during the separation process. In such cases, alternative separation methods, such as tab-routing, may be more appropriate.

Figure 2: V-Scoring
Tab Routing
In this method, tabs are created along the edges of each board. Tab routing is a versatile panelization technique that can accommodate irregularly shaped PCBs and components that extend beyond the edge of the board. For tab routing to work effectively, the tabs must be strong enough to hold the boards securely during assembly and testing, but also thin enough to be easily cut or broken off after assembly.
Sometimes, tabs are routed with additional perforations or stamp holes. These perforations make it easier to separate the individual PCBs from the panel. By breaking off the tabs along these perforations, the stress is evenly distributed across the edge of the PCB, minimizing the risk of damage or deformation.

Figure 3: Tab Routing
In addition to tab routing, breakaway rails can also be included in the panelization design. Breakaway rails are thin strips of material added to the edges of the panel to provide extra support during the manufacturing process. The width of the breakaway rail is typically between 5-8mm. These rails can be easily broken off once the boards have been assembled and tested, leaving the individual PCBs with clean and smooth edges.

Figure 4: Breakaway Rails
If you have any questions regarding PCBs or PCBA, please feel free to contact me at info@wellcircuits.com.