Understanding PCB and PCBA in Electronics Manufacturing
Many individuals often confuse PCB with PCBA in the context of SMT patch processing. So, what exactly is PCB? PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, is a fundamental electronic component that acts as a support and medium for electrical connections of electronic parts. PCBs are commonly known as printed circuit boards and are considered the foundation of electronic products.
Before the advent of PCBs, electronic components were interconnected using wires. However, PCBs revolutionized the industry by providing a more efficient and reliable method of electronic connection, making wires mostly reserved for lab testing purposes.
The PCB production process involves several key steps, including contacting the manufacturer, opening, drilling, copper sinking, graphic handling, graphic plating, film removal, etching, green oil application, character printing, gold-plated finger formation, testing, and final inspection.
Unique Advantages of PCBs
- High density
- High reliability
- Planability
- Productivity
- Testability
- Assemblability
- Maintainability
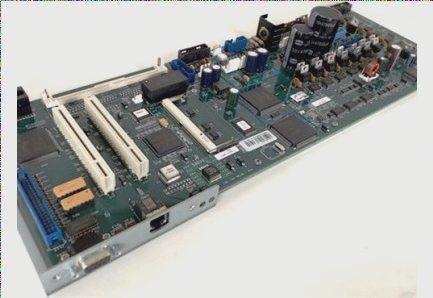
The Evolution of PCBA in Electronics Manufacturing
PCBA, or Printed Circuit Board Assembly, is the process of mounting components onto a PCB using techniques such as SMT (Surface Mount Technology) or DIP (Dual In-line Package). SMT and DIP differ in their component integration methods, with SMT not requiring drilled holes and DIP involving pin insertion into pre-drilled holes.
In SMT processing, small electronic components are mounted on the PCB using a mounter, with steps including PCB positioning, solder paste application, component placement, reflow soldering, and final inspection. Precision in positioning, component size, solder paste quality, and printing is crucial for SMT success.
On the other hand, DIP insertion is utilized for larger components unsuitable for SMT. It involves manual or robotic component insertion, adhesive application, inspection, wave soldering, cleaning, and final inspection.
Understanding the distinction between PCB and PCBA is essential. PCBA represents a fully assembled product circuit board, while PCB signifies an unpopulated board. PCBA is the final product of assembly, whereas PCB is the bare board awaiting components. This differentiation clarifies that PCBA is a completed assembly process.