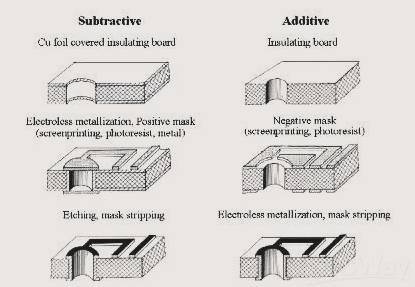
PCB Design Self-Inspection Process
1. Structural Design
- Verify the PCB floor plan and structure diagram.
- Check mounting hole locations and diameters.
- Inspect wiring constraint areas.
2. Component Library
- Confirm component sizes and pin counts.
- Ensure BGA device’s silk screen frame matches DATA SHEET specifications.
- Check component labeling and positioning.
- Verify component positioning holes.
3. Component Layout
- Avoid component overlap.
- Maintain a minimum spacing of 8 mils between components.
- Ensure compliance with no-go zones.
- Place decoupling capacitors near relevant components.
4. PCB Routing
- Comply with no-go area requirements.
- Route adjacent layers perpendicularly.
- Inspect critical signal traces individually.
- Check differential signal trace routing.
5. Solder Mask
- Ensure proper solder mask window sizes.
- Maintain solder mask bridge width.
- Openings for solder mask and paste layer on specific components.
6. Silkscreen Layer
- Avoid silkscreen overlap with pads.
- Properly align silkscreen text.
- Ensure clear and readable silkscreen characters.
7. Vias
- Inspect through-holes for components.
- Consider via capacity for power traces.
- Prevent solder bridging with proper via and pad placement.
8. Gerber Files
- Review Gerber files layer by layer.
- Stack and verify Gerber files.
- Check green oil bridge width in Gerber files.
9. PCB Output File Checks
- Verify PCB schematic diagram and Gerber files.
- Conduct Design Rule Check (DRC).
- Review drilling files and assembly drawings.
The self-inspection process for PCB design involves thorough checks to ensure design accuracy and compliance with standards. For detailed reviews and submissions, it is recommended to assign a dedicated staff member.
If you have any questions regarding PCB design, feel free to contact info@wellcircuits.com.