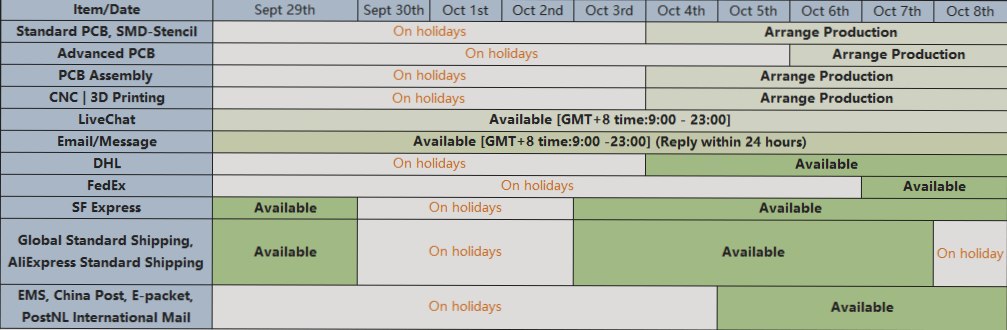
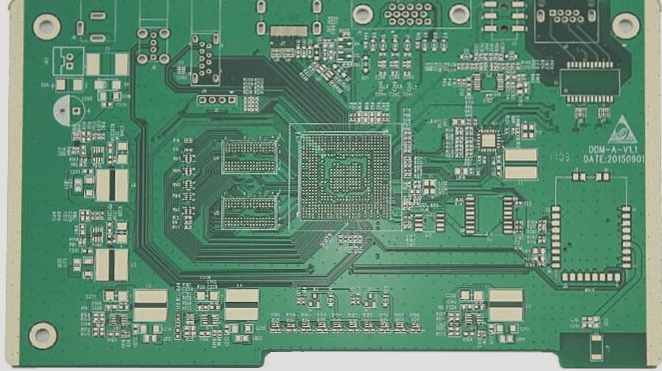
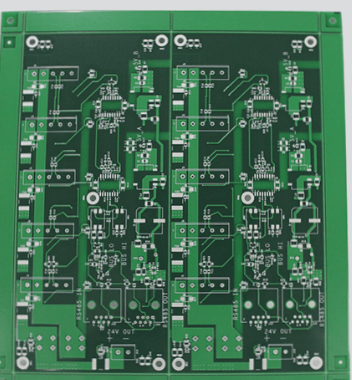
Why is PCBA Testing Necessary?
The process of PCBA involves assembling, connecting, and soldering hundreds of electronic components according to design specifications. Due to slight variations in component parameters, the overall performance can deviate significantly. Additionally, distributed parameters during processing can further impact performance, making it vital to conduct thorough testing to ensure alignment with design requirements.
The Importance of PCBA Testing
PCBA testing is essential to calibrate and evaluate products to meet technical specifications. It identifies design flaws, process defects, and ensures product functionality and quality. This testing process establishes a reliable foundation for assessing electronic devices’ performance parameters.
Key Aspects of PCBA Testing
- Define testing objectives and requirements clearly.
- Accurately select and use testing instruments.
- Adjust and test the PCBA following established procedures.
- Apply circuit and component knowledge to troubleshoot issues.
- Analyze and process data obtained from testing.
- Compile test results and provide recommendations for improvement.
For simpler PCBA assemblies like set-top box modules, testing is direct post-assembly. Complex systems like automotive control units undergo more detailed testing. Testing is typically done in the workshop, following protocols. Large-scale equipment may require preliminary adjustments based on design specifications before final assembly and testing at the installation site.